Major Deserts of Africa
Africa is home to some of the largest and most diverse deserts in the world. These deserts are not just sandy wastelands, as often imagined; they are rich in geological diversity, ecological uniqueness, and even human adaptations.
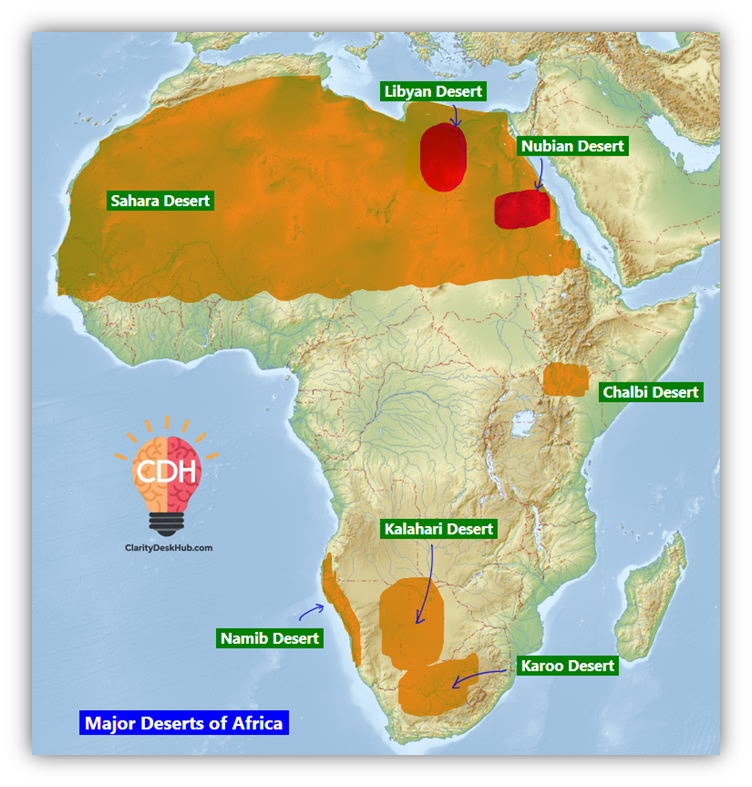
Guys note that a phrase has been provided with each of the deserts just for you to remember the importance of them or quicky you can recall in the exam:
Let’s explore the major African deserts, beginning with the mightiest of them all — the Sahara.
🏜️ Sahara Desert – The Great Sand Sea
📍 Location: North Africa
🌐 Area: ~9.2 million sq. km – World’s largest hot desert, 3rd largest overall (after Antarctica and Arctic)
🔹 Geographical Extent:
- North → Atlas Mountains, Mediterranean Sea
- East → Red Sea
- West → Atlantic Ocean
- South → Sahel region (semi-arid transition zone)
🗺️ Covers parts of 11 countries:
🇩🇿 Algeria 🇱🇾 Libya 🇪🇬 Egypt 🇲🇷 Mauritania 🇲🇱 Mali 🇳🇪 Niger 🇹🇩 Chad 🇸🇩 Sudan 🇲🇦 Morocco 🇹🇳 Tunisia 🇪🇭 Western Sahara
🧭 Key Physical Features:
- Contains rugged mountain ranges:
- Ahaggar Mountains (Algeria)
- Tibesti Mountains (Chad – home to volcanic peaks like Emi Koussi)
- Hosts rocky plateaus, gravel plains, ergs (sand seas), and hamadas (barren rocky areas).
🌡️ Climate Extremes:
- Holds the record for one of the highest temperatures:
Al Azizia (Libya) – 57.7°C in 1922.
💧 Drainage & Rivers:
- Sparse but important:
- Nile River flows through the eastern Sahara.
- Niger River originates in Fouta Djallon (Guinea) and briefly enters southwestern Sahara.
- Ephemeral rivers and wadis (seasonal streams) feed Lake Chad.
🏕️ Human Geography:
- Inhabited by nomadic tribes:
- Bedouins (Arabic-speaking)
- Tuaregs (Berber-speaking, “Blue People” of the desert)
- Presence of oases: self-contained water systems supporting agriculture.
🏞️ Tafilalt Oasis (Morocco) – among the largest self-contained oases in the Sahara.
- (Compare: Al-Ahsa in Saudi Arabia is the world’s largest).
🏜️ Kalahari Desert – The Red Sands of the South
📍 Location: Covers much of Botswana, parts of Namibia and South Africa
🔹 Nature:
- Technically a semi-arid sandy savanna, not a true desert due to more rainfall.
💧 Unique Water Features:
- Only permanent river: Okavango River — forms the Okavango Delta, a unique inland delta teeming with wildlife.
- Salt Pans:
- Makgadikgadi Pan (Botswana)
- Etosha Pan (Namibia)
🌾 Home to the San people (Bushmen) — traditional hunter-gatherers of Southern Africa.
🏜️ Namib Desert – The Living Fossil Desert
📍 Location: Runs along the Atlantic coast of Namibia, Angola, and South Africa
🌐 Length: Over 2,000 km
🔹 Type:
- Cold coastal desert – influenced by the Benguela Current, which causes fog and limits rainfall.
🏞️ Landscape:
- Inland: Gravel plains, rock outcrops
- Coastal: Tall sand dunes — among the highest in the world (e.g., Dune 7, Big Daddy)
🐞 Famous for fog-basking beetles, Welwitschia plant, and desert-adapted elephants.
🏜️ Karoo Desert – A Fossil Time Machine
📍 Location: South Africa
📌 Type: Semi-desert – divided into Great Karoo and Little Karoo
🔹 Key Features:
- Barren terrain with scrub vegetation.
- Renowned for fossil deposits, especially of prehistoric reptiles and therapsids (ancestors of mammals).
🔬 Karoo rocks are critical in understanding the Permian-Triassic extinction.
🏜️ Nubian Desert – Desert of Sand and Stone
📍 Location: Northeastern Sudan and southeastern Egypt
🔹 Boundaries:
- North → Egypt
- East → Red Sea
- South → Nile River
- West → Libyan Desert
🏞️ Landscape:
- Dominated by rocky terrain and sandstone plateaus, unlike the typical sandy Sahara.
- Some dunes are present but less extensive.
👥 Inhabitants:
- Home to Nubian nomads, who have adapted to its harsh environment for centuries.
🏜️ Libyan Desert – Sahara’s Most Inhospitable Part
📍 Location: Northeastern Sahara
- Covers parts of eastern Libya, southwestern Egypt, and northwestern Sudan
🔹 Topography:
- Barren, dry, and rugged.
- Features bare rocky plateaus, stone plains, and sand sheets.
🗻 Notable Peak:
- Mount Al-ʿUwaynat (1,934 m) — located at the tri-junction of Libya, Egypt, and Sudan.
🌬️ One of the driest regions on Earth — practically rainless for years.