Depositional Landforms in Coastal Geomorphology
When the sea deposits sediments along the coastline, it creates depositional landforms. These landforms transform coastlines and influence human settlements, tourism, and marine biodiversity.
Beaches and Dunes
- Beaches:
- Found along coastlines where deposition of sand, gravel, and pebbles dominates.
- These sediments are brought by rivers, streams, or wave erosion and deposited on the shore.
- Even along rugged (ऊबड़ – खाबड़) coastlines, small patches of beaches can form.
- Sand Dunes:
- Formed just behind the beach when winds lift sand particles from the beach and deposit them inland.
- On low sedimentary coasts, these dunes may form long, continuous ridges parallel to the coastline.
✅ Why Important?
- Beaches act as natural buffers against sea waves, protecting coastal lands.
- Sand dunes stabilize the coast and prevent inland erosion.
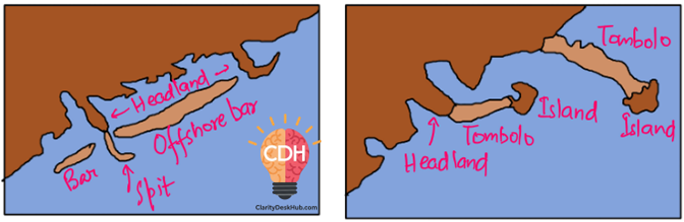
Bars, Barriers, and Spits
- Offshore Bar:
- Imagine a narrow ridge of sand or pebbles formed parallel to the coastline, but inside the sea.
- These are called offshore bars and act as a barrier against high waves.
- Barrier Bar:
- When an offshore bar gets exposed above the water level due to continuous deposition, it becomes a barrier bar.
- These often form at the mouth of rivers or the entrance of bays, protecting inland waters from strong sea waves.
- Tombolo:
- If a bar connects two landmasses, such as connecting an island to the mainland, it is called a Tombolo.
- Example: Adam’s Bridge (Ram Setu) between India and Sri Lanka.
- Spit:
- Sometimes, a bar extends from the coastline but does not completely block the bay, leaving one side open.
- This is called a Spit.
- Example: Chilika Lake Spit along Odisha’s coast.
✅ Why Important?
- Barrier bars protect low-lying coastal areas from storm surges.
- Spits create natural harbors and protect coastlines.
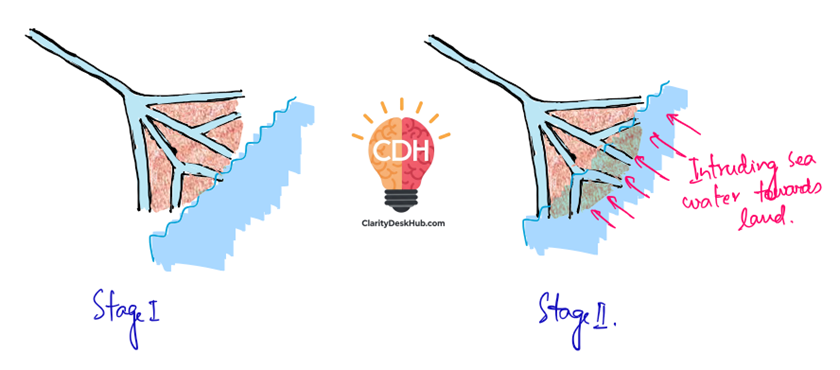
Ria Coasts
- Ria Coast:
- Imagine a river valley near the coast that gets submerged by rising sea levels — this creates a Ria Coast.
- It appears as a drowned river valley but remains open to the sea.
- Most Rias have a dendritic pattern (branch-like) inherited from the river’s drainage pattern.
- Formation:
- When sea levels rise or land subsides, river valleys close to the coast get partially submerged, creating a ria coastline.
- Example: Goa and Konkan Coast exhibit Ria features.
✅ Why Important?
- Ria coasts provide natural harbors for ships and fishing activities.
- They increase coastal tourism due to their scenic beauty.
✅ Why Should We Care About These Landforms?
- Natural Protection: Barrier bars, spits, and beaches protect inland areas from storm surges and coastal erosion.
- Tourism and Economy: Ria coasts, beaches, and sand dunes attract millions of tourists, boosting the economy.
- Harbor Development: Many natural harbors (like Mumbai Port) owe their existence to these coastal formations 🌊
