Other Important Geographical Features of Africa
Africa’s geographical identity is not limited to deserts, rivers, and mountains. It also hosts transition zones, strategic waterways, tectonic depressions, and rare geopolitical landmarks. These features are vital from both a geophysical and geo-strategic perspective.
Please note that Major features of African continent has already been discussed separately
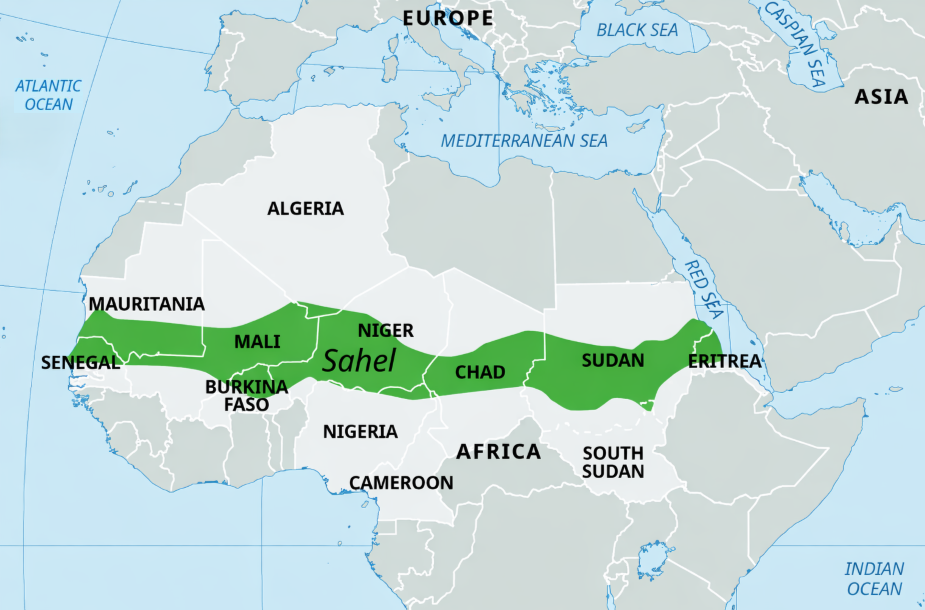
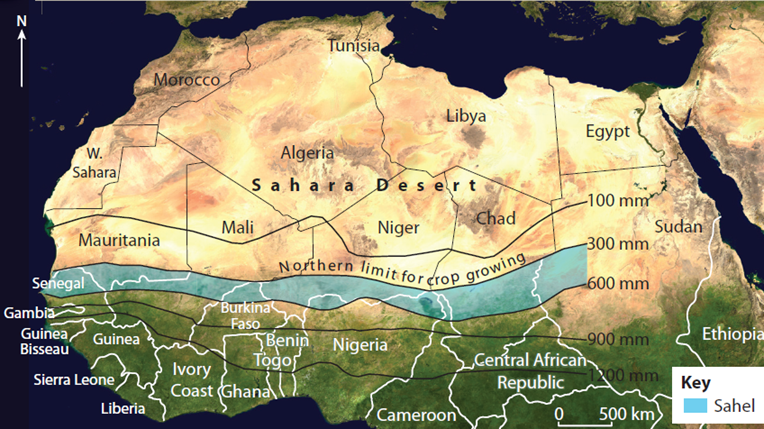
🏜️ Sahel Region
📍 Location: East–West belt just south of the Sahara Desert
🔹 Nature:
- A semi-arid transitional belt between the Sahara Desert (north) and tropical savannas (south).
- Terrain: Mix of sandy, rocky lands with sparse grasslands and drought-resistant trees (e.g., acacia, baobab).
🗺️ Stretches across:
→ From Atlantic Ocean to Red Sea, through:
Northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, south of Algeria, Niger, north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic, central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea, and the extreme north of Ethiopia
🧭 Significance:
- Ecologically fragile, affected by desertification.
- A hotspot for climate-induced migration, pastoralist conflicts, and terrorist insurgency zones (e.g., Boko Haram, Sahel G5).
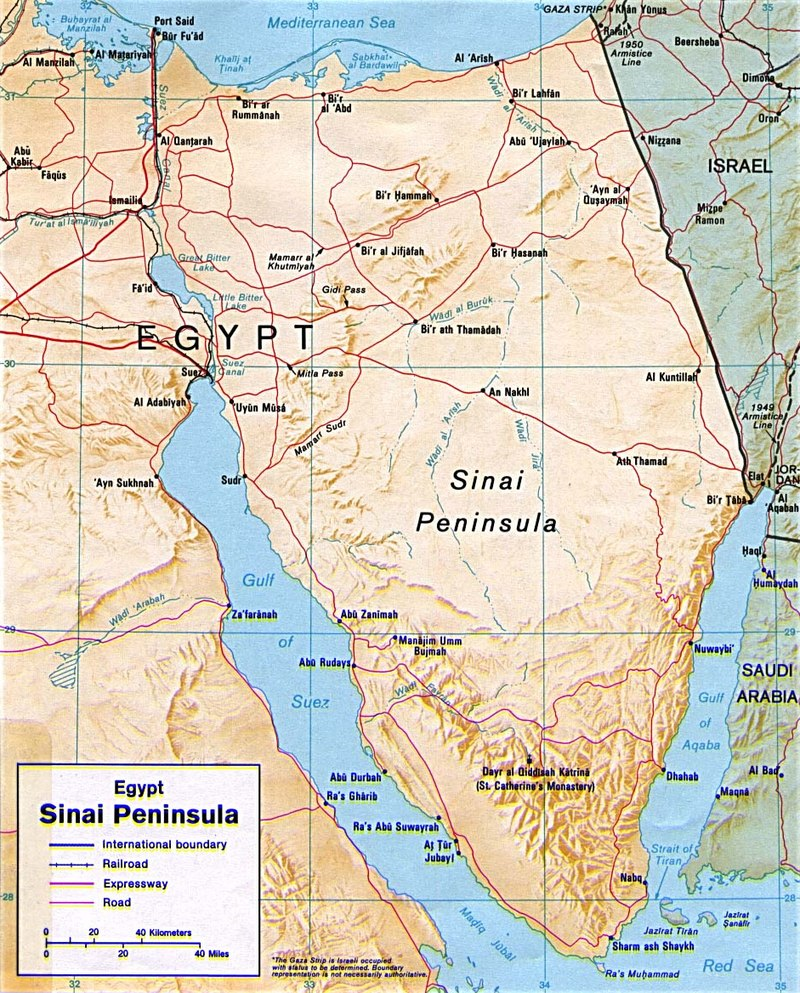
🏞️ Sinai Peninsula
📍 Location: Northeastern Egypt, acting as a bridge between Africa and Asia
🔹 Borders:
- Mediterranean Sea (N),
- Red Sea (S),
- Gulf of Aqaba (SE),
- Israel (E)
- Divided from mainland Egypt by the Suez Canal.
🔹 Historical & Strategic Value:
- Site of historical conflicts (e.g., 1967 Six-Day War, 1979 Egypt-Israel Peace Treaty).
- Returned to Egypt in 1982 after Israeli occupation.
🛣️ Trick to Remember: “Sinai = Suez Near Asia–Israel”
🚢 Suez Canal
📍 Location: Isthmus of Suez, connecting Mediterranean Sea to Red Sea
🔹 Why Important?
- Shortest sea route from Europe to Asia — avoids long route around Cape of Good Hope.
- Geopolitical flashpoint during Suez Crisis (1956) when Egypt nationalised the canal.
🔹 Today:
- Owned by Egypt’s Suez Canal Authority.
- Major revenue source for Egypt and a choke point in global trade.
⚓ Mnemonic: “Suez = Shortcut for Ships from Europe to East”
🌊 Red Sea
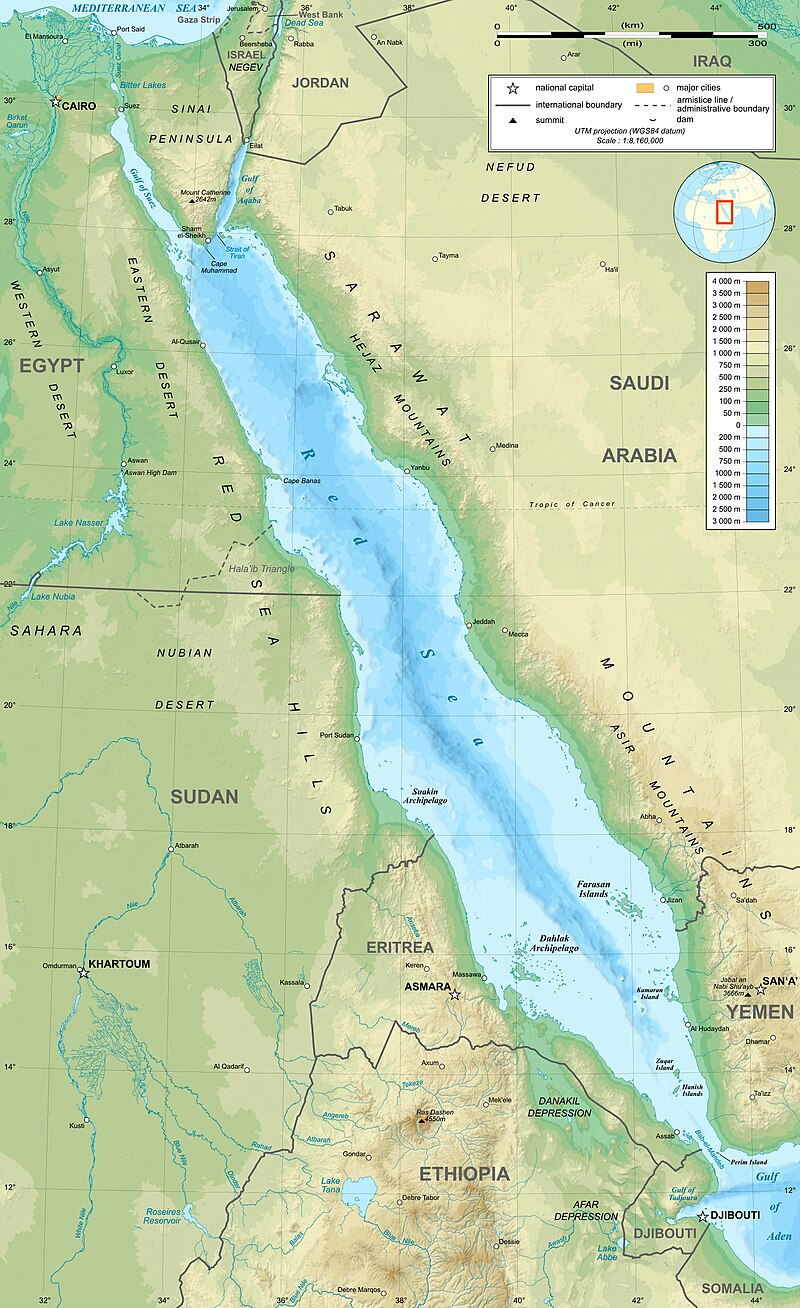
📍 Location: Between Northeast Africa and Arabian Peninsula
🔹 Borders:
- West: Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti
- East: Yemen, Saudi Arabia
🧠 Trick: “Y-SEEDS” → Yemen–Sudan–Eritrea–Egypt–Djibouti–Saudi Arabia
🔹 Geological Nature:
- A Rift Valley Sea — formed by divergence of Arabian and African plates.
- North Red Sea splits into:
- Gulf of Suez (shallow)
- Gulf of Aqaba (deep)
🌋 Also prone to volcanic activity and sea-floor spreading.
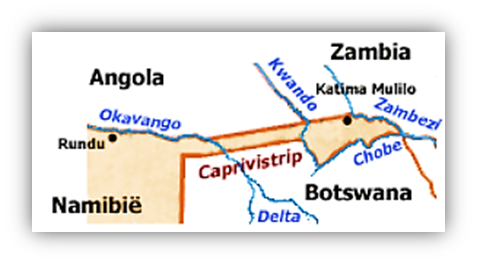
🗺️ Caprivi Strip
📍 Location: Northeastern Namibia
🔹 Shape & Geography:
- A narrow ~450 km extension toward the Zambezi River.
- Borders Angola (N), Botswana (S), Zambia (NE) — lies on swampy plains near the Kalahari’s northern edge.
🧭 Geopolitical Trivia:
- Only known international quadripoint:
→ Where borders of Namibia, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Botswana almost meet (Kazungula region).
🗺️ Definitions:
- Tripoint: Where 3 countries meet — 175 worldwide
- Quadripoint: Where 4 countries meet — extremely rare
🌋 Danakil Depression (Afar Triangle)
📍 Location: At the junction of Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Djibouti
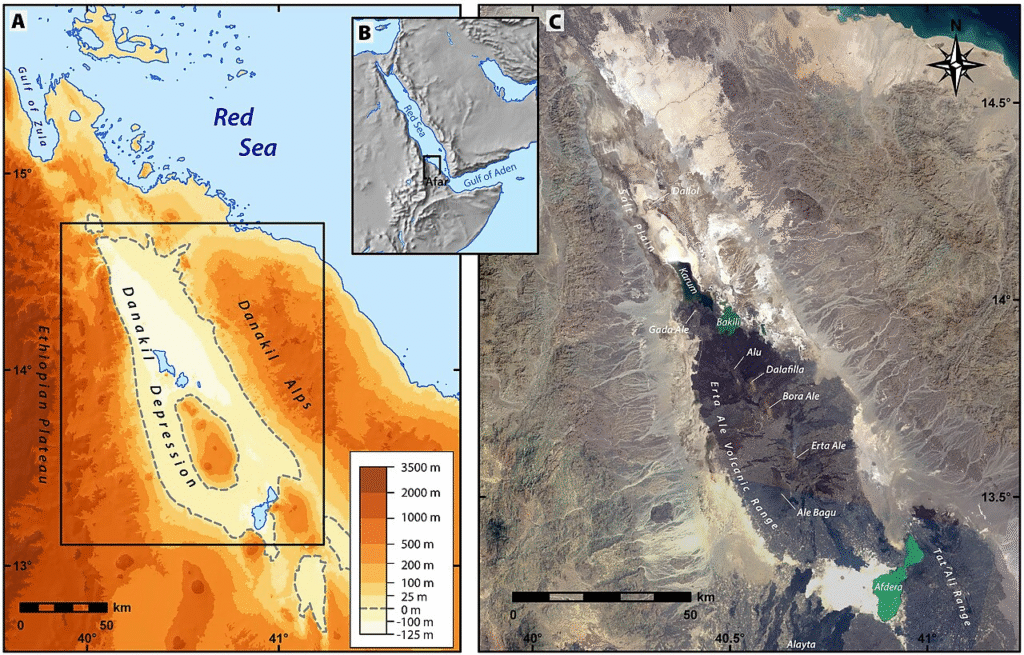
🔹 Geological Significance:
- A tectonic triple junction where African, Somali, and Arabian plates diverge.
- Among the hottest, lowest, and driest places on Earth.
🔹 Key Features:
- Salt flats, acidic hot springs, sulfur pools, and Erta Ale volcano with active lava lake.
- Dallol Crater – extremely acidic springs studied for extremophile microbes (Mars-analog).
🔹 Human Evolution Site:
- Discovery of “Lucy” (Australopithecus afarensis) in 1974 — a key fossil in human evolutionary studies.
🧬 Danakil = Where tectonics, life origins, and evolution intersect

4 Comments