Geographical Regions of Europe
Europe’s geography is not just about landforms—it’s a tapestry of geopolitical identities, cultural regions, and strategic peninsulas, seas, and plains.
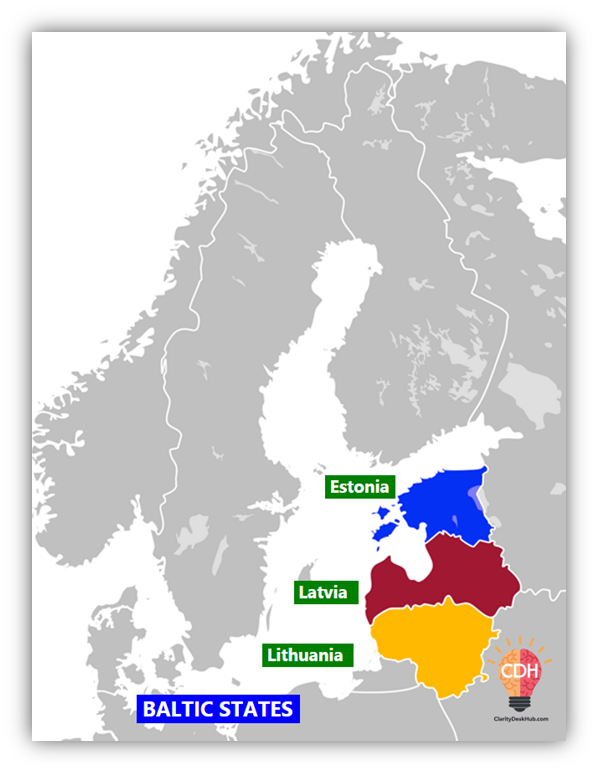
Baltic States
Members: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania
Location: Eastern coast of the Baltic Sea
Key Features:
- Independent but collaborate on defense and economy
- NATO, EU, OECD, Eurozone members
- Buffer states between Western Europe and Russia
- Historically first to exit the USSR in 1990
🧠 Baltics = Trio of democratic post-Soviet states, firmly pro-West.
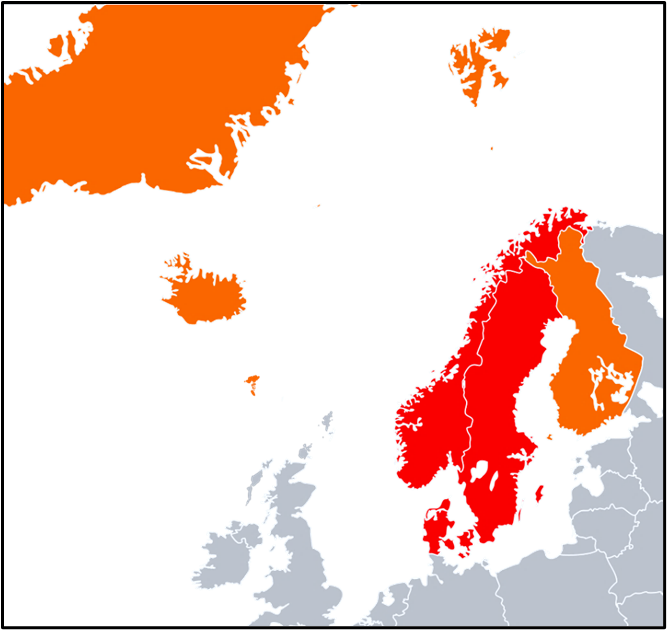
❄️ Nordic Region
| Term | Composition | Notes |
| Scandinavian Peninsula | Norway, Sweden, part of Finland | Physical landform |
| Fennoscandia | Scandinavia + Finland + NW Russia (Karelia, Kola) | Geological region |
| Nordic Countries | Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Iceland + Greenland, Faroe Islands | Cultural-political grouping |
| Scandinavia (in English) | Norway, Sweden, Denmark | Based on language and culture |
🧠 Scandinavia is narrower, Nordic is broader; think of “Nordic” as the entire cold North.
They are known for:
- Welfare models, secularism, high HDI
- Renewable energy leadership
- Strong geopolitical coherence despite linguistic diversity
🇷🇺 Former USSR European Countries
| Region | Countries |
| Baltic | Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania |
| Eastern Europe | Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova |
🧠 All were part of the Soviet sphere, but the Baltics are now firmly Western-aligned.
Belarus and Russia retain strong authoritarian and pro-Moscow alignment, while Ukraine and Moldova lean westward geopolitically.
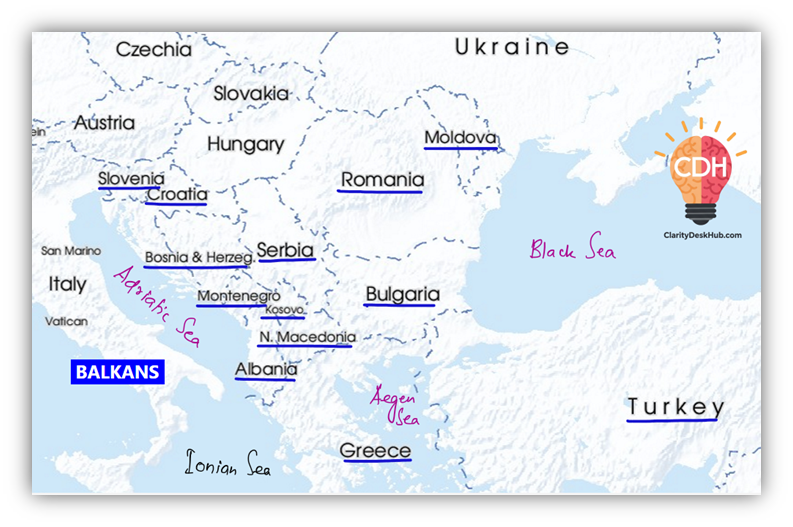
🏔️ Balkans (Balkan Peninsula)
Surrounded by: Adriatic Sea (W), Mediterranean (S), Aegean (SE), Black Sea (E)
Core Countries:
- Albania, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, N. Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia
- Sometimes includes Moldova, parts of Turkey (European part) and Greece
🧠 Balkanisation = Fragmentation based on ethnic fault lines (e.g. breakup of Yugoslavia)
Culturally diverse, linguistically complex, strategically located.
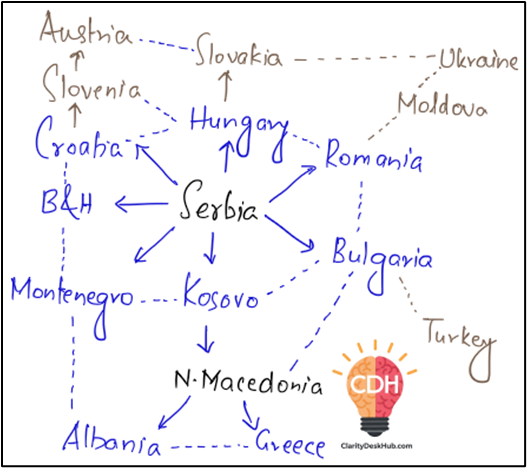
See guys in the overall European map, the region surrounding Balkan region is the most difficult to remember, so I have designed a simple diagram so that you can remember them a bit easily.
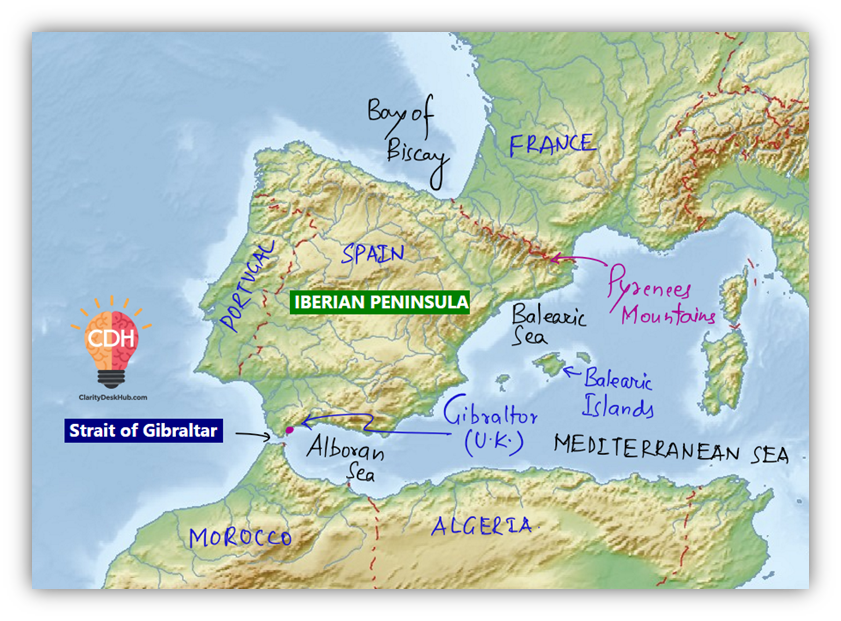
🌄 Iberian Peninsula
Countries: Spain, Portugal, Andorra, Gibraltar (UK), Southern France
Boundaries:
- South: Strait of Gibraltar (to Africa)
- North: Pyrenees Mountains (to France)
🗺️ Meseta Central: High plateau covering 75% of the peninsula
🧠 Iberia = Latin Europe meets the Atlantic and Africa. Mix of European and Moorish heritage.
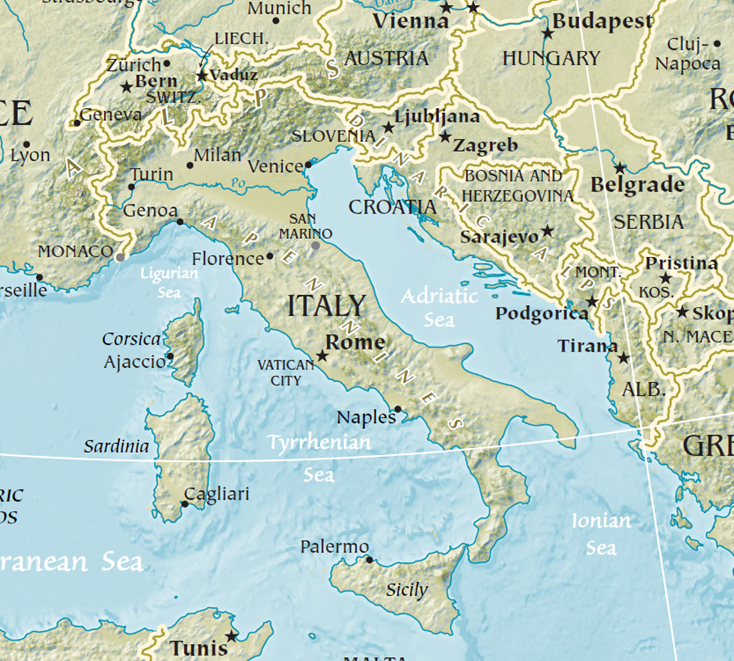
🇮🇹 Italian Peninsula (Apennine Peninsula)
Countries Included: Italy, San Marino, Vatican City
Boundaries:
- East: Adriatic Sea
- South: Ionian Sea
- West: Tyrrhenian and Ligurian Seas
🧨 Mount Vesuvius (near Naples): Only active volcano on mainland Europe
🧠 Peninsula shaped like a boot. Politically fragmented in history, culturally rich.
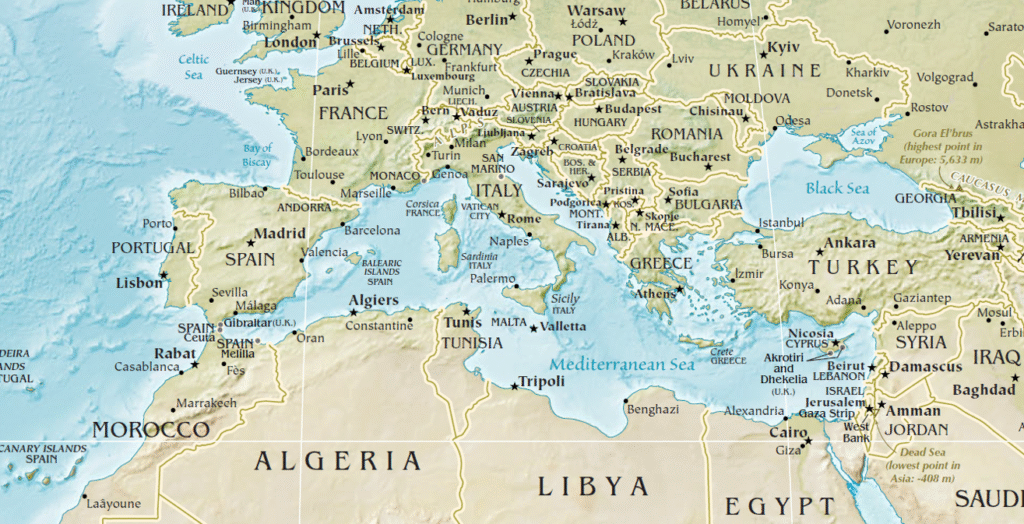
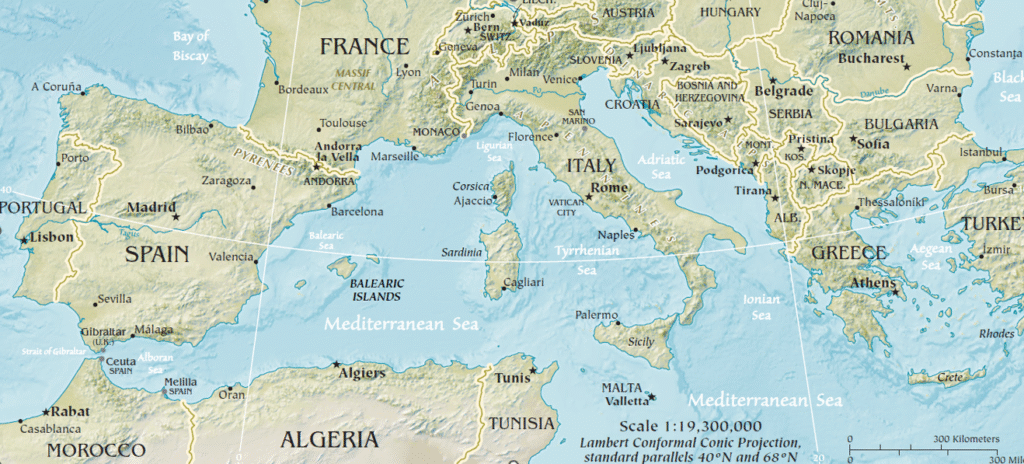
🌊 Mediterranean Sea
– A Bridge Between 3 Continents
Connects to:
- Atlantic: via Strait of Gibraltar (13 km wide)
- Black Sea: via Bosporus → Sea of Marmara → Dardanelles
- Red Sea/Indian Ocean: via Suez Canal → Bab el-Mandeb → Gulf of Aden
🧭 Physiographic Divisions:
A submarine ridge between Sicily and North Africa splits the sea into the Western and Eastern Mediterranean.
Western Mediterranean
- Alborán Basin (Spain–Morocco)
- Algerian Basin
- Tyrrhenian Basin (Italy–Sardinia/Corsica)
Eastern Mediterranean
- Ionian Basin (Italy–Greece, deepest ~4,900 m)
- Levantine Basin (Turkey–Libya)
- Aegean Sea (Greece–Turkey, island-dense)
- Adriatic Sea (Italy–Balkans)
🧠 Mediterranean = Cradle of Civilizations + Strategic chokepoint for naval and trade routes
🦐 Wadden Sea (UNESCO Heritage)
- Location: Intertidal zone along Netherlands, Germany, Denmark
- Feature: World’s largest tidal flats system
- Ecological Significance: Important for migratory birds, coastal biodiversity
🧠 Unique geomorphology; eco-tourism and conservation hotspot.
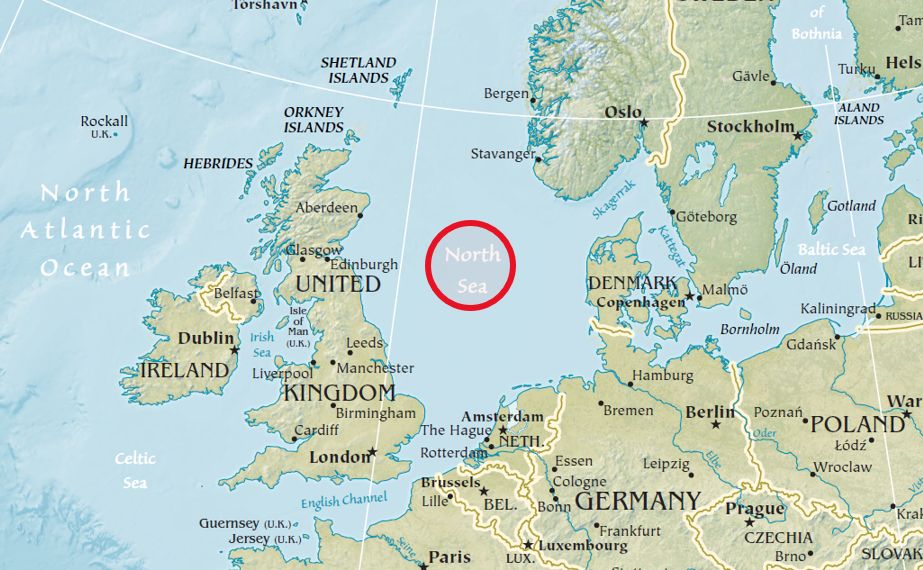
🌬️ North Sea
Boundaries:
- West: England, Scotland
- East: Denmark, Norway, Germany
- South: Belgium, Netherlands, France
Features:
- Connects to Atlantic via English Channel and Strait of Dover
- Major ports: Rotterdam, Hamburg, London
- Rich in:
- Oil & gas (UK, Norway)
- Fishing
- Wind energy (renewable hub)
🧠 North Sea = Europe’s energy basket + trade corridor
🔁 Quick Mnemonic Tools:
- Baltic States: EL-Latvia
(Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania – north to south) - Scandinavia: N-S-D (Norway, Sweden, Denmark)
- Iberian vs Italian Peninsulas:
- Iberia = Iberia Sees Portugal (Spain + Portugal)
- Italy = Boot with Vatican + San Marino
🇾🇪 Erstwhile Yugoslavia
– The Complex Balkan Puzzle
Origin:
- Formed in 1918 as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes → renamed Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929
- Became a socialist republic under Tito post-WWII (1946)
Constituent Republics:
- Bosnia & Herzegovina – Muslim majority
- Croatia – Catholic
- Macedonia (North Macedonia) – Orthodox
- Montenegro – Orthodox
- Serbia – Orthodox
- Slovenia – Catholic
Autonomous Regions under Serbia:
- Vojvodina
- Kosovo (now partially recognized independent state)
Reasons for Disintegration:
- Ethno-religious fault lines (Orthodox vs Catholic vs Muslim)
- Language diversity (South Slavic dialects)
- Economic crisis & weakening of communist unity
- Rise of nationalism post-Tito
Outcome: Seven countries now exist:
- Bosnia & Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovenia
🧠 Yugoslavia = A cautionary tale of ethno-political fragility
Are Yugoslavia and the Balkan Countries the Same? Not Quite.
Many students assume that former Yugoslavia and the Balkan countries are synonymous, but this is a common misconception. While they overlap geographically, they differ in origin, nature, and scope. Here’s a comparison to understand the distinction clearly:
| Aspect | Former Yugoslavia | Balkan Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Historical-political entity | Geographical and cultural region |
| Timeline | Existed from 1918 until the early 1990s | Exists to this day as a defined region |
| Composition | 6 republics (Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia) + 2 autonomous provinces (Kosovo and Vojvodina)* | Around 12 countries (varies slightly based on definitions) |
| Identity | Federal socialist state with dominant Slavic identity | Multi-ethnic, multi-religious, and multi-lingual diversity |
| Status | Dissolved after civil wars and political breakup | Continues to be geopolitically and culturally relevant |
*Note: Kosovo declared independence from Serbia in 2008 but is not universally recognized.
🌉 Turkish Straits
– Europe-Asia Connector
Key Straits:
- Bosphorus: Black Sea → Sea of Marmara
- Dardanelles: Sea of Marmara → Aegean Sea
Strategic Importance:
- Maritime chokepoints—control access to Black Sea
- Boundary between Europe and Asia
- Governed by Montreux Convention (1936)—limits naval passage in peacetime/war
🧠 Turkey = Gatekeeper of Eurasian geopolitics
🟩 Great European Plain
– The Breadbasket and Highway
Extent: Pyrenees (West) → Urals (East)
- Narrow in West (~320 km) → Widens in Russia (~3,000 km)
Divisions:
- North European Plain: France to Poland
- Eastern European Plain (Russian Plain): Poland → Ural Mountains
Significance:
- Most agriculturally productive region
- Site of historic invasions (e.g., Napoleon, Hitler) due to flat terrain
🧠 A continuous corridor—economic, agricultural, and military
🟨 Pannonian Basin
– Central European Depression
Enclosed by: Carpathians & Transylvanian Alps
- Dominated by the Great Hungarian Plain
- Danube River cuts it in half
🧠 Fertile basin + river connectivity = agricultural and trade hub of Central Europe
🌟 Unique Geographical Concepts of Europe
🛡️ Polders – Dutch Water Mastery
- Reclaimed lowlands from sea by dikes + pumps
- Netherlands: Global leader in polderization
- Soil desalination required for agriculture
🧠 Turning sea into land = Dutch engineering marvel
🌿 Machair – Atlantic Eco-zone
- Fertile, grassy plains on western Scottish and Irish coasts
- Formed by shell sand blown inland
- Important for traditional crofting and biodiversity
🧠 Nature-culture symbiosis in Atlantic fringe
🍌 Blue Banana – Industrial Power Curve
- Urban-industrial corridor from SE England → Belgium → Netherlands → Germany → Switzerland → Northern Italy
- Named for:
- Shape (banana curve)
- Colour (EU blue; industrial identity)
🧠 Blue Banana = European economic heartland
🔁 Quick Recap Mnemonics
| Region/Concept | Mnemonic |
| Yugoslavia’s breakup | BBC-MMSSK: Bosnia, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Slovenia, Kosovo |
| Turkish Straits | “BoDa”: Bosphorus → Dardanelles |
| European Plain | France to Urals = Flat & Fertile |
| Polder vs Machair | Polder = Dutch dike land, Machair = Celtic shell plains |
| Blue Banana | 🍌 = Blue for EU, Banana for shape (from UK to Italy industrial belt) |
🌐 Mapping Utility
- Yugoslavia breakup = essential for Balkan mapping
- Turkish Straits = draw clear Europe-Asia divide
- European Plain = understand Napoleonic and Nazi invasions
- Pannonian Basin = locate Danube’s mid-course
- Blue Banana = plot urban-industrial axis
- Polders = shade reclaimed Netherlands coastlines

5 Comments