Industrial Regions of North America
To understand North America’s industrial geography, imagine a land blessed with:
- Natural wealth: rich deposits of coal, iron ore, petroleum
- Early European colonization: laying the foundation for industrial towns
- Urbanized society: creating a large labour market and consumer base
- Superb transport: think Great Lakes, Mississippi River, Transcontinental Railways, Interstate Highways
In short, nature provided the raw materials, history provided the push, and technology ensured success.
Major Industrial Regions in North America
Let’s now understand these regions one by one like a geographical jigsaw puzzle—each piece has its own identity but fits into the bigger industrial picture.
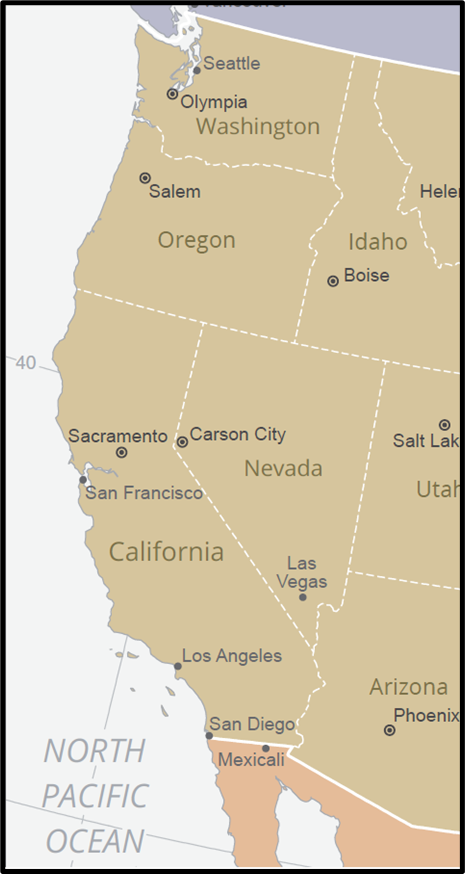
Before going into details have a look at political map of USA so that you can locate the cities mentioned easily:
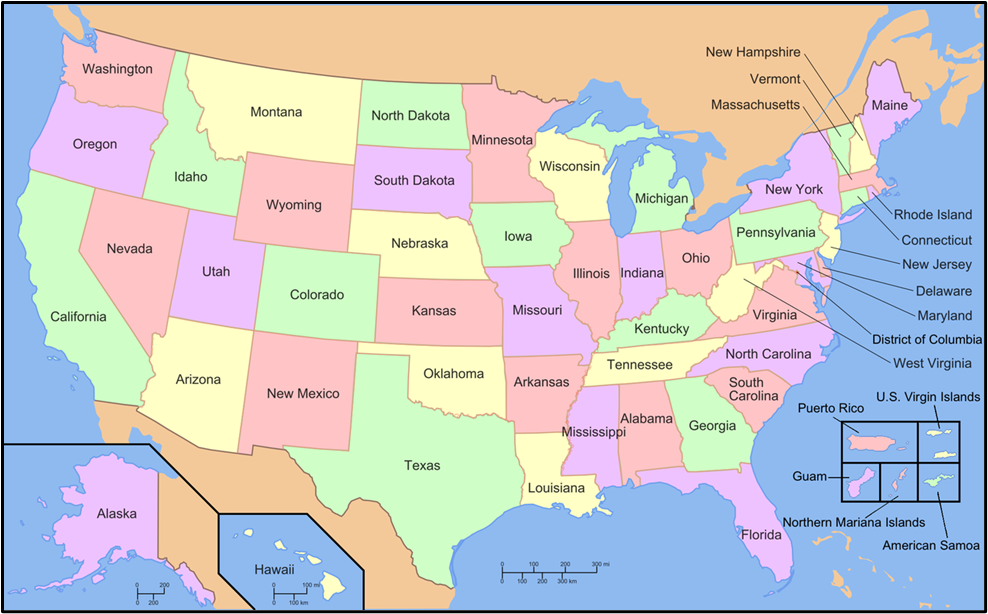
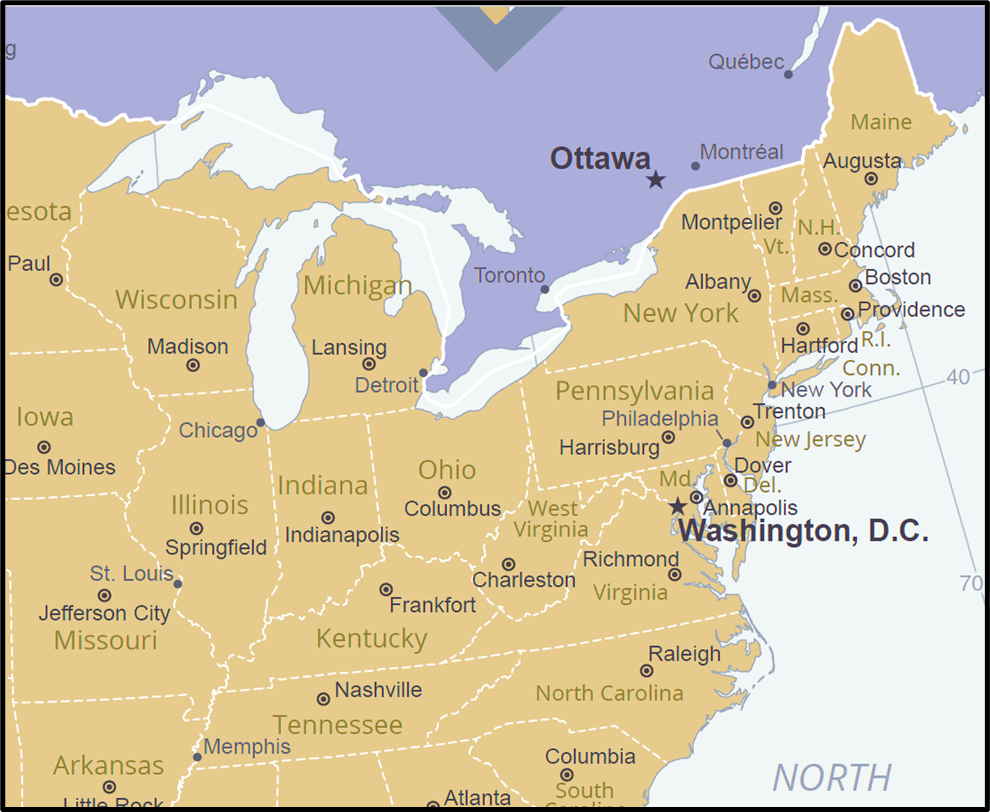
🔹 A. Northeastern USA (The Manufacturing Belt / Rust Belt)
📍Where?
From New York to Illinois via Pennsylvania, Ohio, Michigan etc.
📌 Key Features:
- America’s oldest and most diversified industrial belt
- Located near Appalachian coalfields and Great Lakes
- Dense urban-industrial centers: Detroit, Chicago, Pittsburgh
🏭 Industries:
| City | Specialization |
|---|---|
| Pittsburgh | Iron & Steel |
| Detroit | Automobiles (Ford, GM) |
| Cleveland | Chemicals, Machinery |
| Chicago | Meatpacking, Rail Equipment |
| Buffalo | Hydroelectric-powered industries |
📉 Recent Trend:
Due to outdated infrastructure and rising costs, industries began shutting down—leading to the term “Rust Belt”. Many industries moved southward to the Sunbelt.
🔹 B. Mid-Atlantic Industrial Region
📍Where?
New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore, Newark
📌 Highlights:
- Very densely populated → cheap and ample labour
- Anthracite coal from Pennsylvania
- Global ports → strong trade connections
🏭 Industries:
Textiles, chemicals, publishing, processed foods, and also finance—Wall Street!
🔹 C. Great Lakes Industrial Region
Note: This region overlaps with the Manufacturing Belt but is often categorized separately due to its focus on heavy industries using lake transport routes.
📍Where?
Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, Milwaukee, Gary
📌 Advantages:
- Iron ore from Lake Superior
- Coal from interior USA
- Waterways like the St. Lawrence Seaway for shipping
🏭 Industries:
- Steel, cement, glass, machinery
- Chicago: Transport hub
- Milwaukee: Tools, beer
It’s an industrial corridor with water, iron, coal, and transport—all in one place.
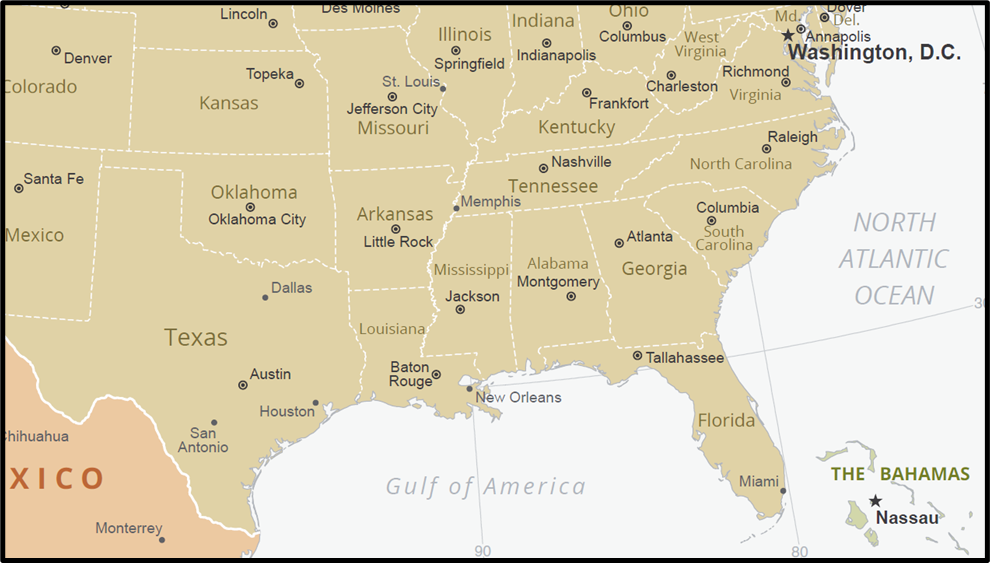
🔹 D. Southern USA (The Sunbelt)
📍Where?
Texas, Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, Alabama
📈 Why growing?
- Lower wages and taxes
- Non-unionized, flexible labour
- Newer industries: aerospace, IT, oil
🏭 Key Zones:
| Region | Specialization |
|---|---|
| Texas (Houston, Dallas) | Oil, petrochemicals, aerospace |
| North Carolina | Textiles, furniture |
| Florida (Orlando) | Tourism, aerospace |
| Alabama (Birmingham) | Steel, chemicals |
The Sunbelt is like a rising star—less rusty, more shiny.
Sunbelt is a broader demographic-economic region characterized by warmer climate, low taxes, and rapid urban-industrial growth, particularly in aerospace, defense, and IT.
🔹 E. Pacific Coast Industrial Region
📍Where?
Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, San Diego
📌 Why important?
- Trans-Pacific port access (key for trade with Asia)
- Hub for aerospace, tech, and creative industries
🏭 Industries:
| City | Specialization |
|---|---|
| Los Angeles | Aerospace, film (Hollywood), electronics |
| San Francisco | Biotech, software (Bay Area) |
| Seattle | Boeing (aircraft), Microsoft (software) |
This is the high-tech frontier of America—globally connected, innovation-driven.
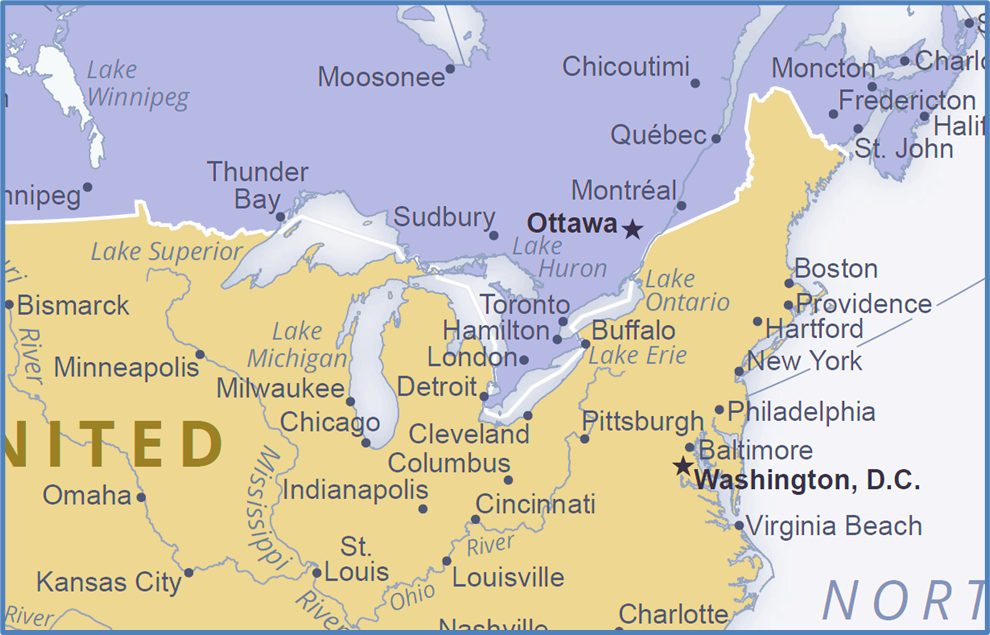
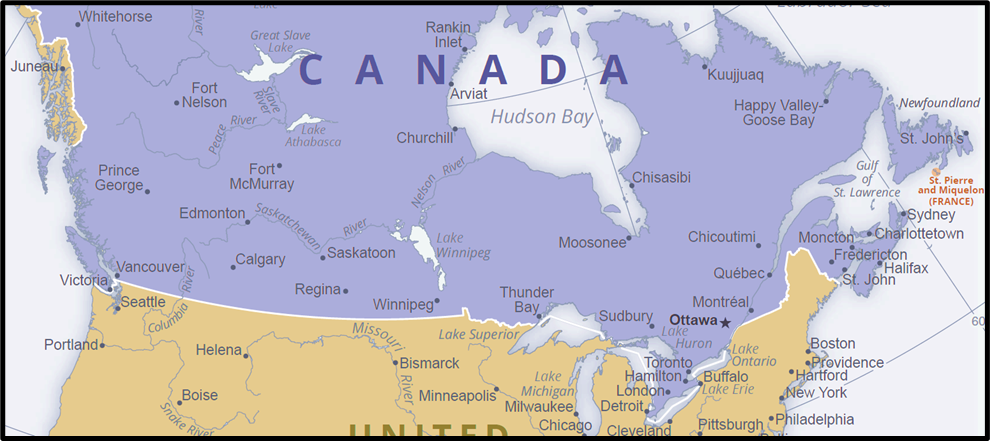
🔹 F. Canadian Industrial Regions
1. Ontario–St. Lawrence Valley
📍Cities: Toronto, Hamilton, Montreal, Ottawa, Quebec
- Hamilton → Steel
- Quebec → Pulp & Paper
- Windsor → Automobiles
- Powered by hydroelectricity and skilled labour
2. Prairie Region
📍Cities: Calgary, Edmonton, Winnipeg
- Agro-based and oil refining
- Alberta’s Tar Sands = treasure chest of oil
3. British Columbia Coastal
📍Cities: Vancouver, Prince Rupert
- Forestry, machinery, pulp & paper
- Pacific port advantage
- Vancouver is a major Pacific trade port facilitating lumber and mineral exports to Asia
Factors Influencing Industrial Location in North America
Let’s understand this:
| Factor | Why Important |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Appalachia (coal), Lake Superior (iron), Texas & Alberta (oil) |
| Water Transport | Great Lakes, Mississippi River, St. Lawrence → move heavy goods easily |
| Labour Supply | Urban east + immigrant cities = large workforce |
| Capital & Technology | Venture capital, R&D, Silicon Valley mindset |
| Market Demand | Dense cities = big consumer base |
| Policy Support | NAFTA/USMCA, tax incentives, export zones |
This shows how geography + policy + innovation combine to shape industrial patterns.
🔄 Contemporary Trends
North America’s industrial geography is not static. It’s evolving rapidly:
- 🌞 Sunbelt is rising: Cheaper and newer
- 💻 High-tech hubs booming: Silicon Valley (CA), Austin (TX), Raleigh (NC)
- 🌱 Greener industries emerging due to environmental regulations
- 🤝 Economic integration with Canada & Mexico under USMCA (formerly NAFTA)
- Many US industries have relocated manufacturing units to Northern Mexico (e.g., Maquiladoras near US border) due to cost advantages under USMCA.
🧭 Map Pointer Strategy (for UPSC Mapping)
Visualise this for better recall. Here’s what to mark:
- Great Lakes Cluster: Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland
- North Atlantic Seaboard: New York, Boston, Philadelphia
- California Axis: San Francisco to San Diego
- Texas Triangle: Dallas–Houston–San Antonio
- Canada: Toronto–Montreal Corridor
UPSC doesn’t just ask where these are—they want you to know why they are there.
I will suggest you to locate these places on the maps provided in this section. If you do these kinds of exercises, I am sure it will get imprinted in your conscious/ sub-conscious memory and you will be able recall in a better way in exams.
🧠 Final Takeaway
North America’s industrial story is like a living organism—shaped by resources, markets, policies, and now technology and environment. From the Rust Belt to Silicon Valley, it reflects a journey of transformation and adaptation.
If you’re aiming for UPSC, don’t just mug up city names. Understand the logic—why that city? What resources? Which industry? What trend?
