Important Concepts of Solar System UPSC/IAS
🌠 What’s the Closest Star to the Sun?
Let’s go beyond our Sun now and meet its closest neighbours in the galaxy.
🔸 Proxima Centauri
- Distance: 4.2 light-years (ly) away.
- It’s a red dwarf and the nearest known star to the Sun.
- Part of the Alpha Centauri triple-star system:
- Alpha Centauri A – slightly bigger & brighter than the Sun
- Alpha Centauri B – slightly smaller
- Proxima Centauri – closest, but dimmest.
📝 Fun Fact: It has been the closest star for the last 32,000 years, and will remain so for another 33,000 years. After that, Ross 248 will take over.
🔸 What Can You See Without a Telescope?
- Northern Hemisphere: Closest visible star is Sirius (Dog Star) — 2nd brightest after the Sun.
- Southern Hemisphere: Alpha Centauri is visible.
- Proxima Centauri is too dim to see without a telescope.
Astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars using stellar parallax. By observing a star from two opposite points in Earth’s orbit—six months apart—they detect a tiny shift in the star’s apparent position relative to distant background stars. This angular shift helps calculate distance using basic trigonometry.
🛑 Heliopause – Where Does the Solar System End?
There is no physical wall or line marking the end of the solar system, but there is a scientifically agreed-upon boundary.
🌀 Solar Wind vs. Interstellar Medium
- Solar Wind: A flow of charged particles from the Sun.
- Interstellar Medium: Thin gas (mostly H and He) in space.
Where these two meet, there’s a tug-of-war that defines the boundary of the solar system.
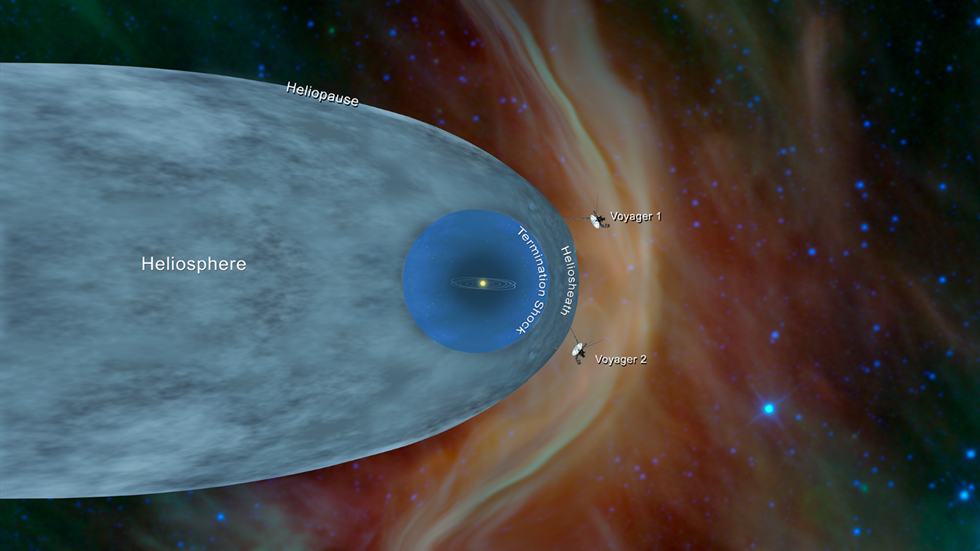
💡 Key Zones:
| Zone | Description |
| Heliosphere | Bubble-like region filled with solar wind, enclosing the entire solar system |
| Termination Shock | Inner boundary — where solar wind slows below sound speed |
| Heliosheath | Transitional zone between termination shock and heliopause |
| Heliopause | Outer boundary — where solar wind stops and interstellar pressure dominates |
| Bow Shock | Like a wave in front of a moving boat, caused by the Sun’s motion through space |
🛰️ Voyager Milestones:
- Voyager 1: Crossed termination shock at 94 AU, heliopause in 2012
- Voyager 2: Crossed termination shock at 84 AU, heliopause in 2018
🚀 Distant Artificial Explorers — Humanity’s Ambassadors to the Cosmos
📡 The Deep Space Network (DSN)
- NASA’s global communication system to maintain contact with faraway spacecraft.
- Locations: California, Madrid, Canberra
🛰️ Major Space Probes and Their Missions:
| Probe | Launched | Key Events | Status | Distance from Sun (AU) |
| Pioneer 10 | 1972 | Flew past Saturn in 1979 | Contact lost in 2003 | ~120 AU |
| Pioneer 11 | 1973 | Flew past Saturn in 1979 | Contact lost in 1995 | ~90 AU |
| Voyager 1 | 1977 | Entered interstellar space in 2012 | Active | ~155 AU |
| Voyager 2 | 1977 | Entered interstellar space in 2018 | Active | ~129 AU |
| New Horizons | 2006 | Flyby of Pluto (2015); now exploring Kuiper Belt | Active | ~53 AU |
| Juno | 2011 | Studying Jupiter since 2016 | Active | Still within Jupiter’s orbit |
📝 Quick Insight: Voyager 1 is the farthest human-made object from Earth.
