Other Important Geographical Feature of Australia
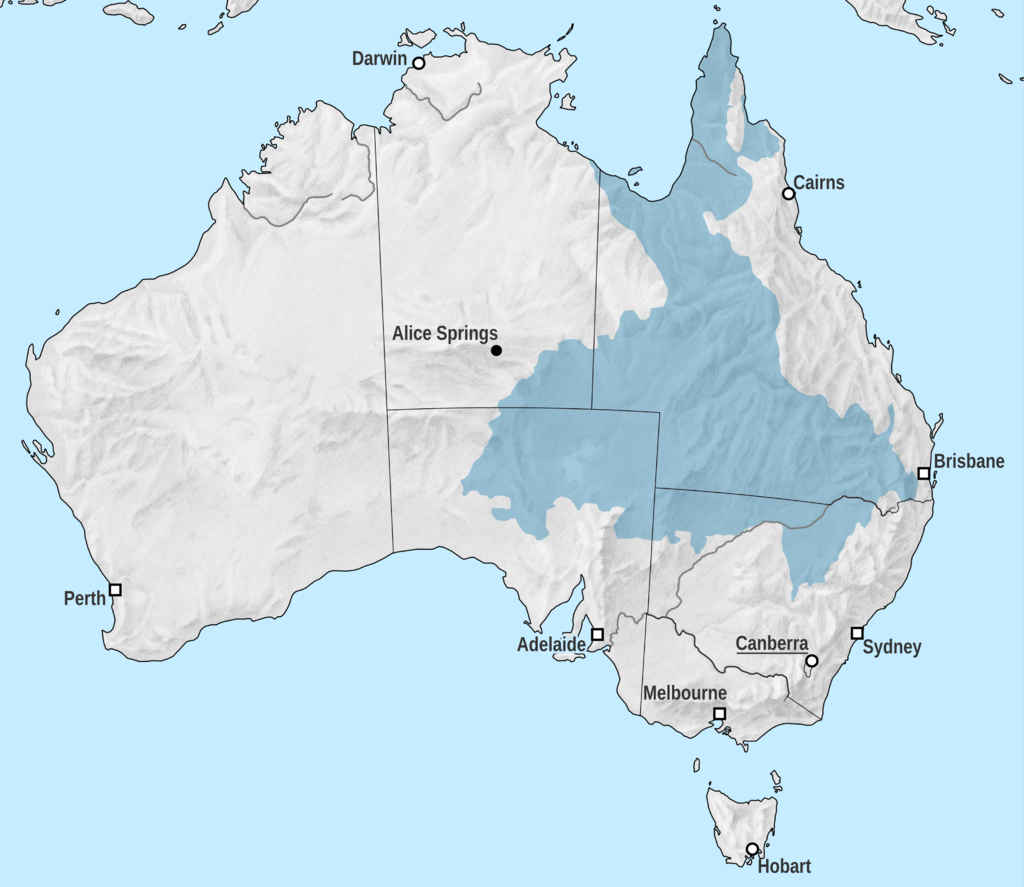
🌊 Great Artesian Basin (GAB)
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| 🔹 Type | Underground hydrogeological system |
| 🔹 Area | ~1.7 million km² (~20% of Australia) |
| 🔹 States Covered | Queensland, NSW, South Australia, NT |
| 🔹 Geological Units | Eromanga, Surat & Carpentaria Basins |
| 🔹 Importance | Supports agriculture, livestock, mining & town water supply |
| 🔹 Discharge | Water seeps out through rock fractures, creating springs and creeks |
🧠 Why important for UPSC?
Because GAB shows how Australia survives its arid heartland—a lifeline in an otherwise dry interior.
via Wikimedia Commons
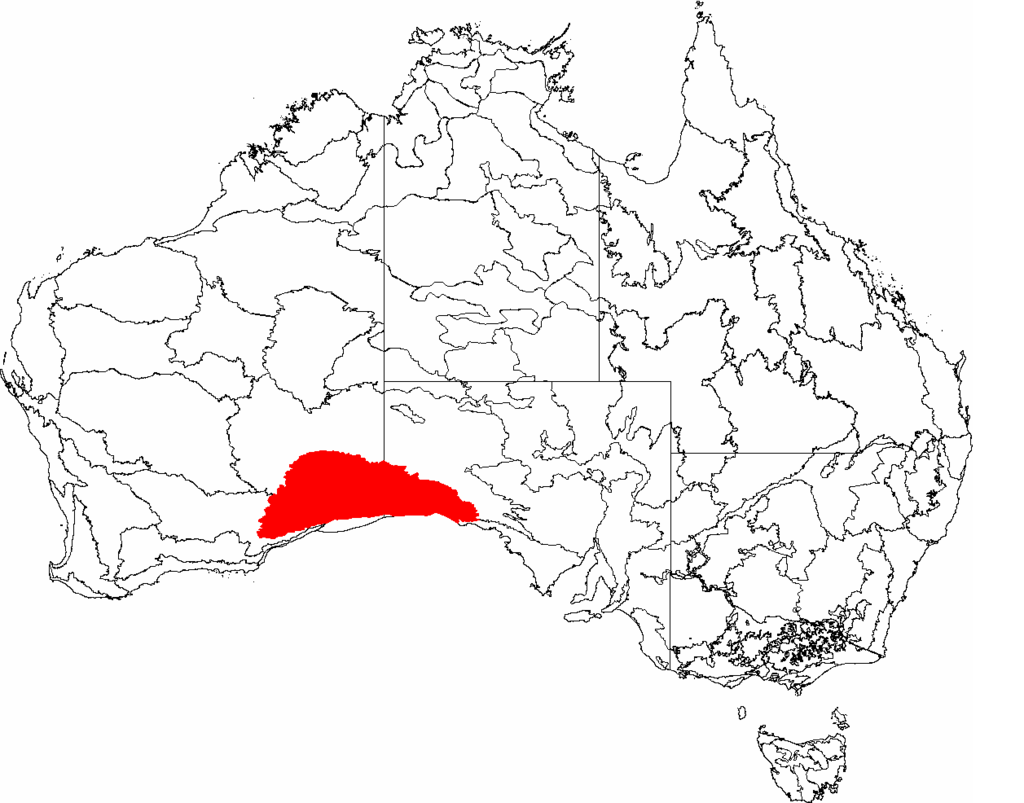
🏞️ Nullarbor Plain
| 🔹Location | Southern Australia (along Great Australian Bight) |
| 🔹 Area | ~270,000 sq. km |
| 🔹 Terrain | Flat, treeless plain (from Latin Nullus Arbor) |
| 🔹 Features | Sinkholes, caves, limestone dents, ancient seabed rock |
| 🔹 Cliffs | Ends at Bunda Cliffs—200 km long sea-facing precipice |
| 🔹 Historical Geology | Wilson Bluff Limestone: Formed when Australia drifted from Antarctica (~65 MYA) |
🧠 Why significant?
It combines geology + geomorphology + historical plate tectonics, all key for UPSC.
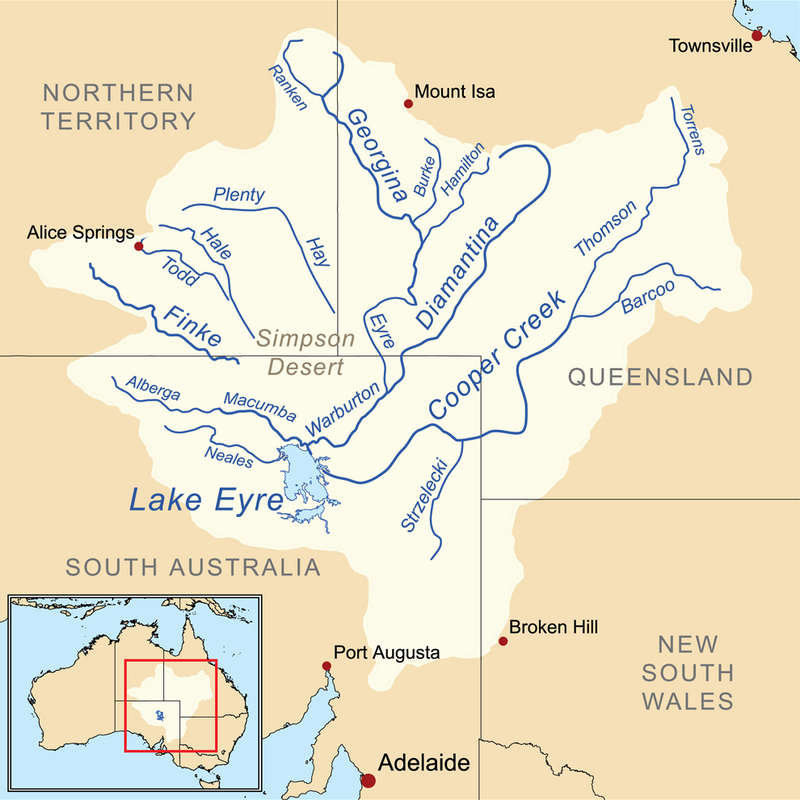
🧂 Lake Eyre
| 🔹 Type | Salt Lake of tectonic origin |
| 🔹 Location | South Australia |
| 🔹 Sections | Lake Eyre North & South (joined by Goyder Channel) |
| 🔹 Elevation | Lowest point in Australia (15 m below sea level) |
| 🔹 Drainage | Endorheic basin (internal); minimal rainfall (<125 mm annually) |
| 🔹 Feature | Intermittent flooding → evaporation → salt crust formation |
🧠 UPSC Prelims Map Alert: Identify the lowest point, endorheic basin, or salt crust lake in Australia? → Lake Eyre
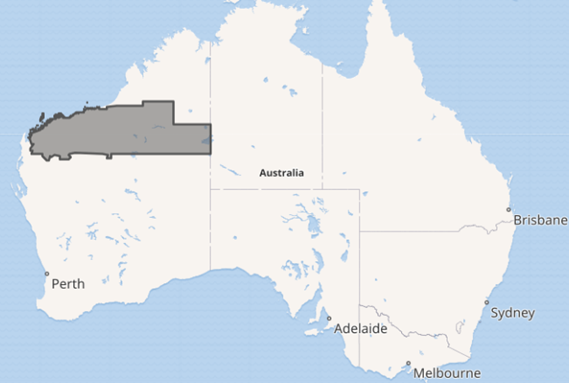
⛏️ Pilbara Region
| 🔹 Location | Western Australia |
| 🔹 Cities | Karratha, Port Hedland |
| 🔹 Key Feature | Iron ore deposits—backbone of Australian mining exports |
| 🔹 Cultural Note | Rich Aboriginal rock art heritage |
🧠 Mains Angle: Connect Pilbara to economic geography—natural resources, mining, trade.
⛰️ Kimberley Plateau
| 🔹 Location | Northern Western Australia |
| 🔹 Geology | Flat sedimentary rocks (sandstone, quartzite), basalt flows |
| 🔹 Minerals | Iron, gold, lead, zinc, silver, diamonds |
| 🔹 Notable Site | Argyle Diamond Mine – one of the largest diamond mines globally |
🧠 Combines plateau formation + mineral resources → high value for both Prelims + Mains.
🪸 Great Barrier Reef
| 🔹 Location | Northeastern Australia (Queensland coast; Coral Sea) |
| 🔹 Length | Over 2,300 km – World’s largest coral reef system |
| 🔹 Biodiversity | 400+ coral types, 1,500+ fish species, 4,000+ mollusc species |
| 🔹 Threatened Species | Dugongs, green turtles |
| 🔹 Concerns | Coral bleaching due to climate change (2018 study: 1/3 severely degraded) |
🧠 UNESCO World Heritage Site
Key topic for Environment, Biodiversity, Climate Change in Mains.
🗾 Tasmania
| 🔹 Type | Island State |
| 🔹 Location | Southeast of mainland Australia, across the Bass Strait (240 km wide) |
| 🔹 Geography | Rugged & mountainous; extension of Great Dividing Range |
| 🔹 Islands | Includes Tasmania, Bruny, King, Flinders, and Macquarie Island |
| 🔹 Climate | Cool temperate climate |
🧠 Think of Tasmania as Australia’s southern cap—rich in biodiversity, scenic beauty, and unique ecological features.
🌊 Great Australian Bight – The Southern Marine Arc
| 🔹 Type | Marine bay-like feature (bight = open curve of coastline) |
| 🔹 Location | Southern coast of Australia |
| 🔹 Biodiversity | 85%+ species are endemic |
| 🔹 Economic Role | Hosts Australia’s largest commercial fishery |
🧠 Map relevance + Biodiversity + Economy = Ideal for both Prelims map-based questions and Mains environmental geography.
🏜️ The Outback
| 🔹 Definition | Remote, sparsely populated inland Australia |
| 🔹 Regions Covered | Arid/semi-arid zones, deserts, ranges (Gibson, Sandy, MacDonnell) |
| 🔹 Land Use | Grazing (sheep & cattle), opal mining, natural gas |
| 🔹 Special Region | Channel Country (floodplains in SW Queensland) |
| 🔹 Famous Landmark | Uluru (Ayers Rock) |
🧠 Term “Outback” has cultural + economic + geographical connotations—important for UPSC Mains.
🪨 Uluru (Ayers Rock)
| 🔹 Type | World’s largest monolith (sandstone formation) |
| 🔹 Location | Central Australia |
| 🔹 Cultural Value | Sacred to Aboriginal people; UNESCO World Heritage Site |
| 🔹 Uniqueness | Changes colour with sunlight (symbol of Australia’s arid beauty) |
🧠 Mains-worthy cultural geography topic—link Uluru to Aboriginal beliefs + tourism.

💧 Billabong
| 🔹 Definition | A waterbody formed when a river changes course—similar to oxbow lake |
| 🔹 Formation | Formed after heavy rains/flooding, isolating a loop of a river |
| 🔹 Use | Often found in arid zones; important for local water availability |
🧠 A culturally rooted term, often appears in Australian literature and geography.

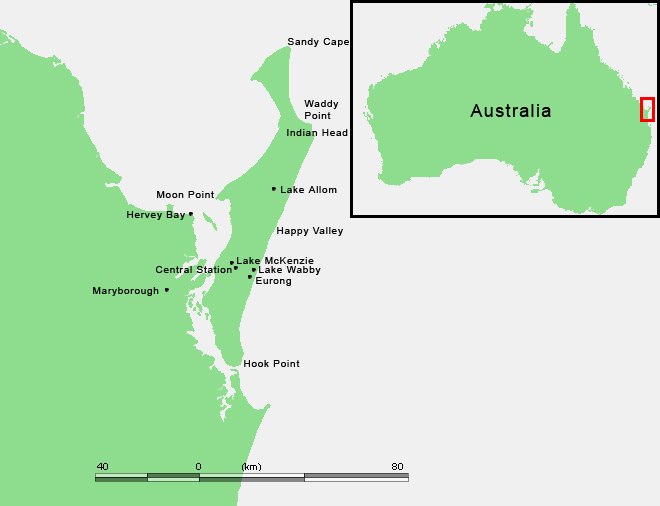
🏝️ K’gari (Fraser Island)
| 🔹 Location | East coast of Australia (off Queensland) |
| 🔹 Type | World’s largest sand island |
| 🔹 Ecosystems | Rainforests on sand, shifting dunes, perched freshwater lakes |
| 🔹 Hydrology | Home to largest unconfined aquifer on a sand island |
🧠 A marvel of geomorphology + ecology—extremely useful for Environment & Biodiversity topics in Mains.
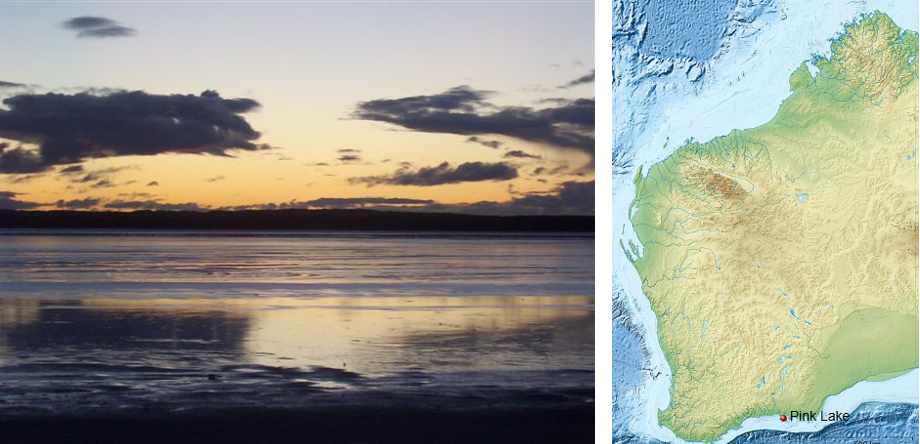
🌸 Pink Lakes
| 🔹 Definition | Natural saline lakes that appear pink due to biological & chemical factors |
| 🔹 Key Microbes | Dunaliella salina (algae producing beta carotene which gives water reddish pink hue) + Halobacteria( emits a red pigment) |
| 🔹 Key Lakes | Lake Hillier (WA), Pink Lakes of Murray-Sunset National Park (Victoria) |
| 🔹 Cause | High salinity + specific microorganisms = pink colour |
🧠 Pink lakes link biogeography + chemistry + tourism—highly relevant for UPSC Environment section.


4 Comments