Other Important Geographical Features of Asia
Please note that all the major Geographical Features of Asia has been discussed separately
Black Sea – A Natural Gateway Between Europe and Asia
Imagine the Black Sea like a huge inland bathtub that’s surrounded by various landforms from three continents. But here’s the twist—it’s meromictic, meaning the water layers don’t mix. The top layer stays on top and the bottom on the bottom—just like oil and water don’t mix easily. This feature makes it ecologically unique.
📍 Location:
- East of the Balkan Peninsula (think of countries like Bulgaria, Romania).
- South of Eastern European Plain
- West of the Caucasus Mountains
- North of Anatolia (modern-day Turkey’s Asian part)
🌊 Connections:
- It doesn’t directly open into the ocean but eventually connects to the Atlantic Ocean through a chain of water bodies:
- Bosporus → Sea of Marmara → Dardanelles → Aegean Sea → Mediterranean → Atlantic
To the north, it meets Sea of Azov via the Kerch Strait.
💧 Rivers:
It receives water from three major rivers: Danube, Dnieper, and Don. These rivers are like lifelines bringing freshwater into the basin.
🌆 Important Cities:
Coastal cities like Istanbul, Odesa, Sevastopol, Burgas, and Batumi make this region geopolitically and economically active.
🌍 Bordering Countries (Mnemonic: Tea and BURGeR):
- Turkey
- Bulgaria
- Ukraine
- Russia
- Georgia
- Romania
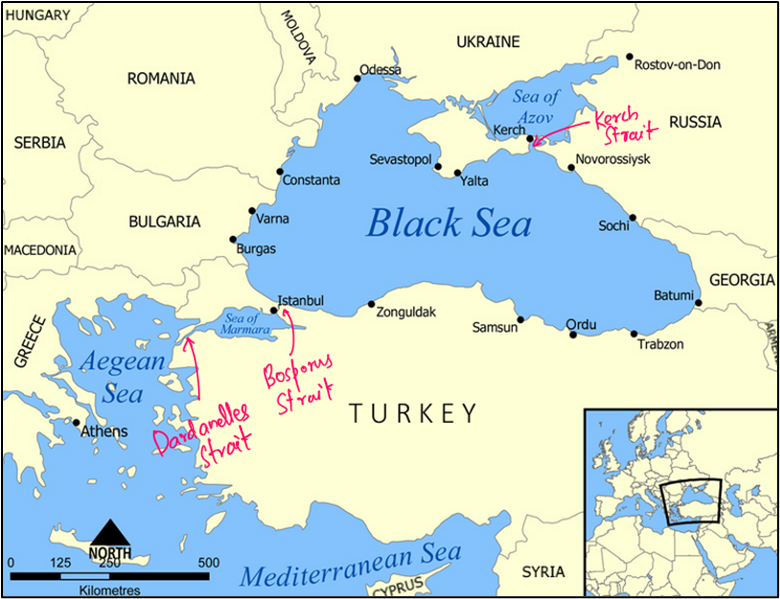
Sea of Marmara – A Maritime Connector and Earthquake Hotspot
It acts like a bridge between continents and is completely within Turkey.
🌐 Role:
- Connects Black Sea and Aegean Sea via Bosporus (Northeast) and Dardanelles (Southwest).
- Facilitates transport of oil and gas from Asia and Russia to Europe.
🌍 Seismic Activity:
The North Anatolian Fault runs below this sea, making the region prone to massive earthquakes.
🌆 Major Cities:
Istanbul, Bursa, Izmit, etc.
🏝️ Marmara Island:
- Turkey’s largest in this sea.
- Known for its marble deposits.
Caspian Sea – The Sea That’s Actually a Lake
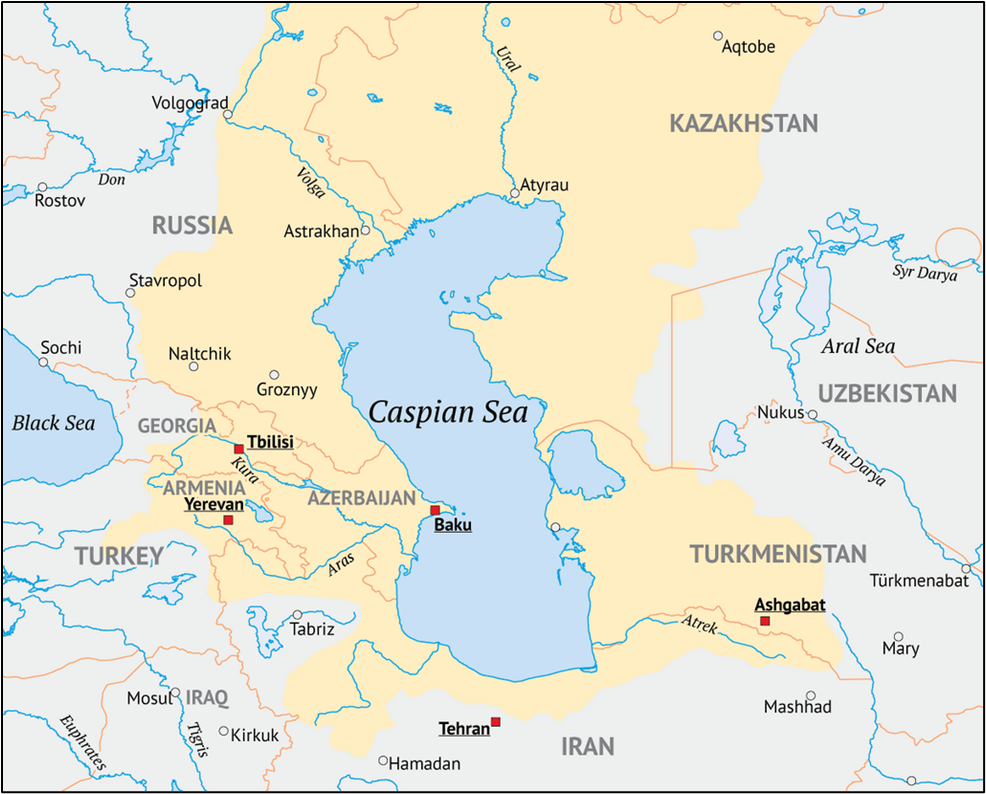
This is the world’s largest inland water body but it behaves like both a sea and a lake.
📌 Key Concepts:
- It is an endorheic basin—no outlet to oceans.
- Brackish water—less salty than ocean but not freshwater.
- Oceanic origin—remnant of the ancient Paratethys Sea, with basaltic oceanic crust.
💧 Inflows:
Primarily fed by the Volga and Ural rivers.
🌍 Bordering Countries (Mnemonic: TARIK):
- Turkmenistan
- Azerbaijan
- Russia
- Iran
- Kazakhstan
⚓ Key Ports:
Baku, Aktau, Astrakhan, Bandar Anzali
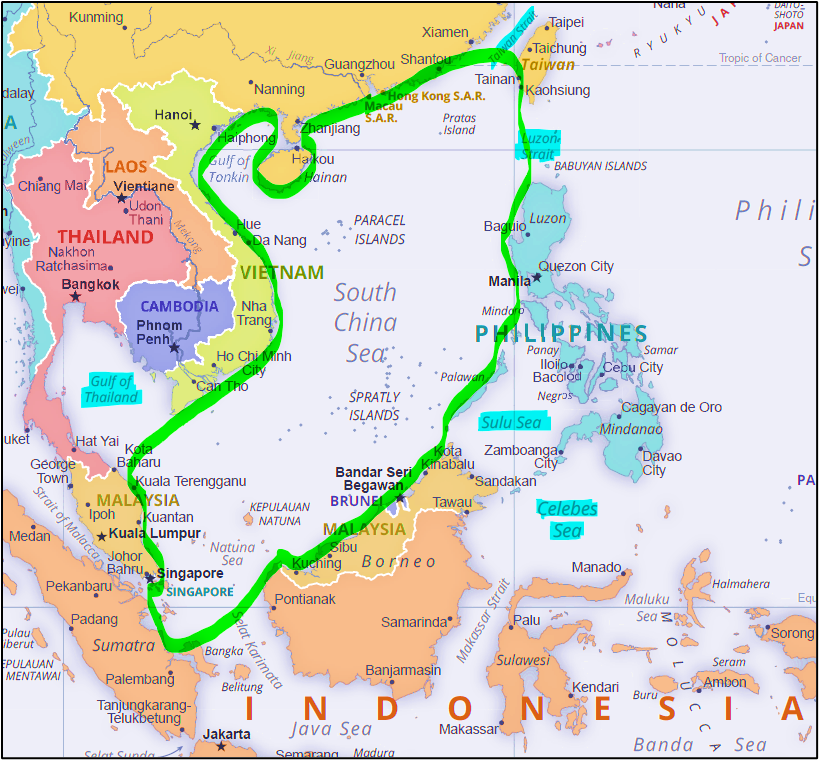
South China Sea – The Maritime Flashpoint
This sea is not just water—it’s wealth, power, and politics all mixed together.
🌐 Location:
Lies in western Pacific, south of China, bordered by Southeast Asian countries.
🌍 Bordering Countries
Mnemonic: VIP China MBT → “Very Important People, China Mein Bade Tareef”:
- Vietnam
- Indonesia
- Philippines
- China
- Malaysia
- Brunei
- Taiwan
🔍 Key Features:
- Eastern Deep Basin: Deep rhombus-shaped region with islands like Paracels, Macclesfield, etc.
- Sunda Shelf: A shallow marine region with ancient river valleys, connecting Vietnam to the Java Sea and Thailand.
⚔️ Dispute:
- China claims 90% of this sea using the controversial “Nine-dash line”.
- Artificial islands & military installations have escalated tensions.
- A tribunal ruling rejected China’s claims, but the issue remains unresolved.
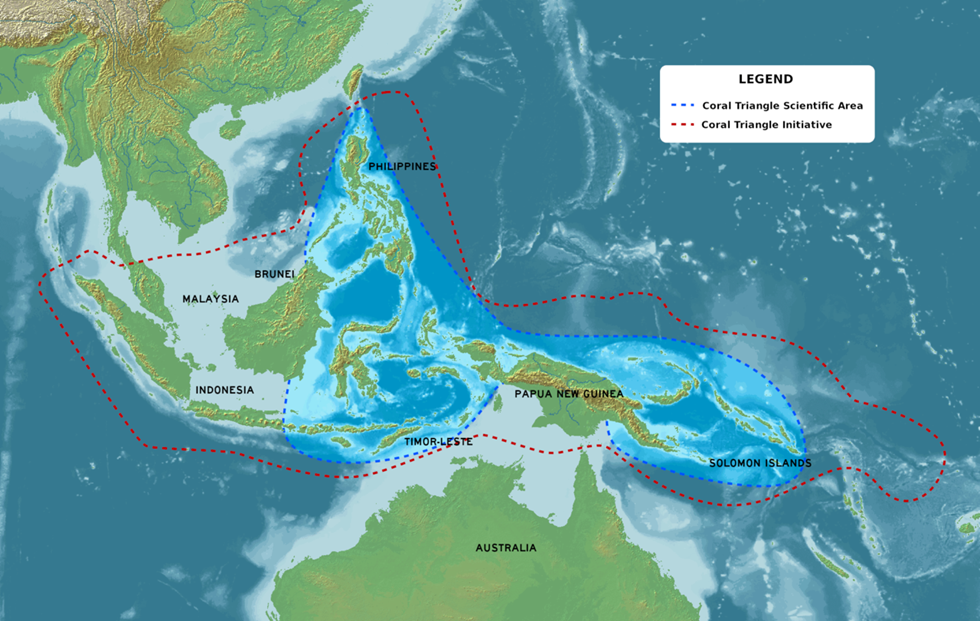
Coral Triangle – The Marine Amazon
Think of this as the Amazon rainforest beneath the ocean, stretching across:
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Papua New Guinea
- Solomon Islands
- Timor Leste
🌊 Richness:
- Houses 76% of all coral species and 37% of coral reef fishes globally.
⚠️ Conservation:
Recognised as a Particularly Sensitive Sea Area (PSSA) by the IMO(International Maritime Organisation), owing to its ecological value.
Eurasian Steppe
A vast, open temperate grassland stretching 8,000 km from Hungary to China.
📍 Divided Into:
| Western Steppe | Eastern Steppe |
| Danube → Black Sea → Volga → Altai | Altai → Greater Khingan → Mongolia/China |
| Includes Pannonian, Pontic-Caspian | Includes Kazakh, Mongolian-Manchurian |
| More stable climate (Ukraine, Romania) | Harsher, irregular rainfall |
| Suitable for easy migration | Oasis-based settlements, mountain streams |
🌿 Flora & Fauna:
- Short grasses like buffalo grass, sagebrush.
- Animals: badgers, hawks, snakes, etc.
Mongolian–Manchurian Grassland
- Situated between Siberia, Central Asian deserts, and Manchurian hills.
- Elevation: 1000–1300 m
- Dominated by feather grass
- Key species: Mongolian gazelle (flagship), wolves, foxes
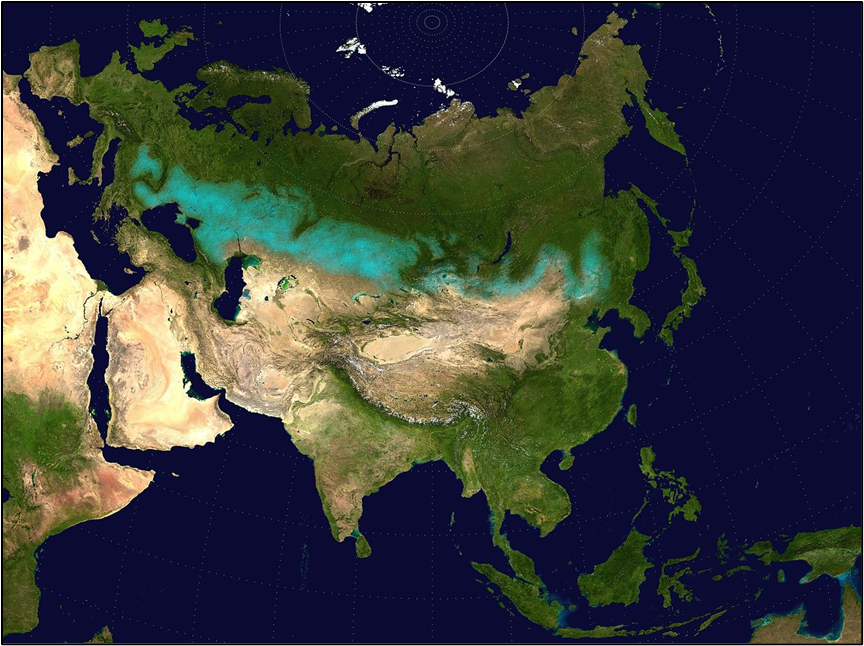
Lake Baikal
Located in Southern Siberia, Lake Baikal is the oldest, deepest, and largest freshwater lake by volume.
🌊 Key Facts:
- Over 1,600 m deep
- Holds 20% of world’s unfrozen freshwater
- Second only to the Caspian Sea in volume
🌱 Biodiversity:
- Baikal Seal – only freshwater seal in the world
- Golomyanka Fish – found only in Lake Baikal
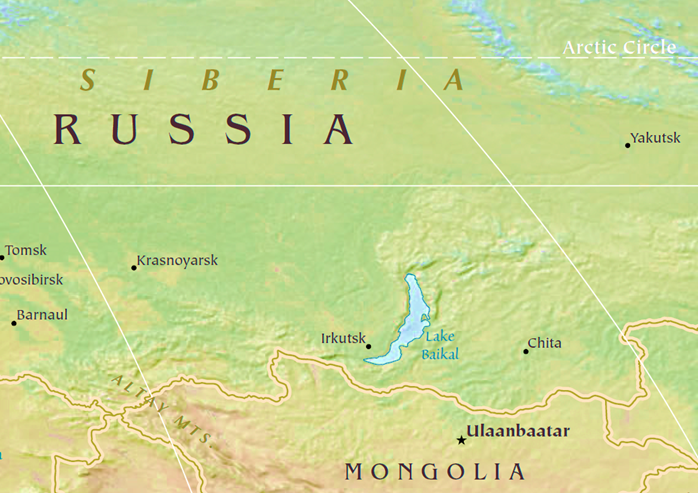
Dead Sea – The Lowest Lake on Earth
The Dead Sea, situated between Israel and Jordan in the Jordan Valley, holds a fascinating record—it is the lowest exposed point on Earth’s land surface, about 420 meters below sea level. But that’s not all—it’s also the saltiest large water body, with 9.6 times more salinity than ocean water.
- This extreme salinity prevents aquatic life and allows people to effortlessly float—thanks to the dense, buoyant water.
- Formed due to tectonic shifts between the African and Arabian plates, it originally got cut off from the Mediterranean.
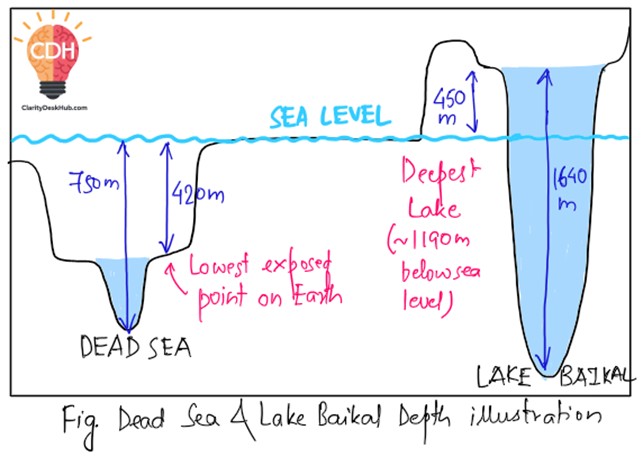
🧠 Concept Clarity: Lowest Point vs Deepest Lake
- Dead Sea: ~420m below sea level (surface) + ~330m depth = ~750m below sea level (lowest land depression)
- Lake Baikal: Surface is ~450m above sea level, depth is ~1640m, so the deepest point lies ~1190m below sea level
Note: Figures have been rounded off for simplicity
You can draw the following diagram in exams to enhance your answers:
Aral Sea – A Shrinking Disaster
The Aral Sea, once the world’s 4th largest lake, lies between Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. But it’s notorious today as a classic example of human-made environmental disaster.
- Since the 1960s, the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers feeding this endorheic salt water lake were diverted for Soviet irrigation.
- Result? The lake has shrunk drastically, devastating local climate, fisheries, and communities.

Tibetan Plateau – The Roof of the World
This is the world’s highest and largest plateau, formed due to the collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates.
- Known as the “Roof of the World”, it’s so high it affects global atmospheric circulation by reversing the Hadley cell and driving the Indian Monsoon.
- It includes Tibet, parts of Ladakh and Western China, and is bounded by Himalayas (south), Kunlun (north), Karakoram (west).
- The Tibetan Plateau is called the “Third Pole” as it holds the largest freshwater reserve outside polar regions.
- Rivers like the Yangtze, Yellow, and Brahmaputra originate from here.
Deccan Plateau – Ancient Volcanic Marvel
The Deccan Plateau forms the bulk of peninsular India, nestled between the Western and Eastern Ghats.
- It contains the Deccan Traps, formed by volcanic eruptions 66 million years ago.
- Rich in minerals: mica, iron ore (Chota Nagpur), diamonds, gold (Golconda).
- Its volcanic basalt base and layered lava flows are geologically significant.
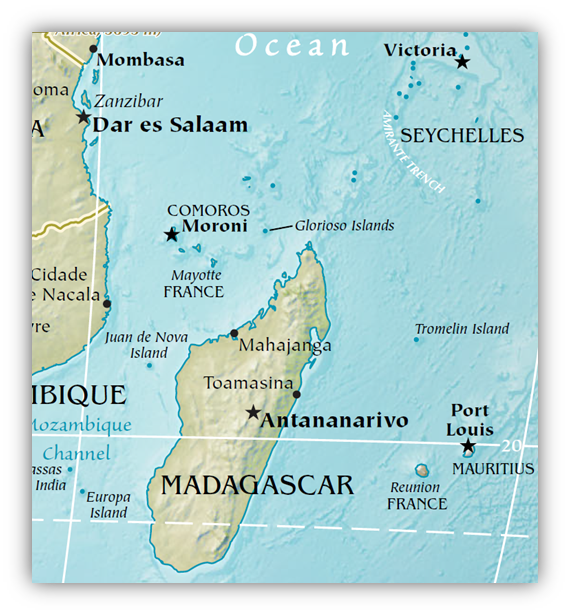
Mascarene Plateau – Hidden Underwater Legacy
Located in the Indian Ocean, between the Seychelles and Mauritius, this is a submarine or oceanic plateau, shaped like a crescent.
- The northern part has granitic rock from Gondwana, topped with limestone and basalt from Deccan eruptions.
- The southern part is volcanic, shaped by the Réunion hotspot, with now-submerged shoals and banks.
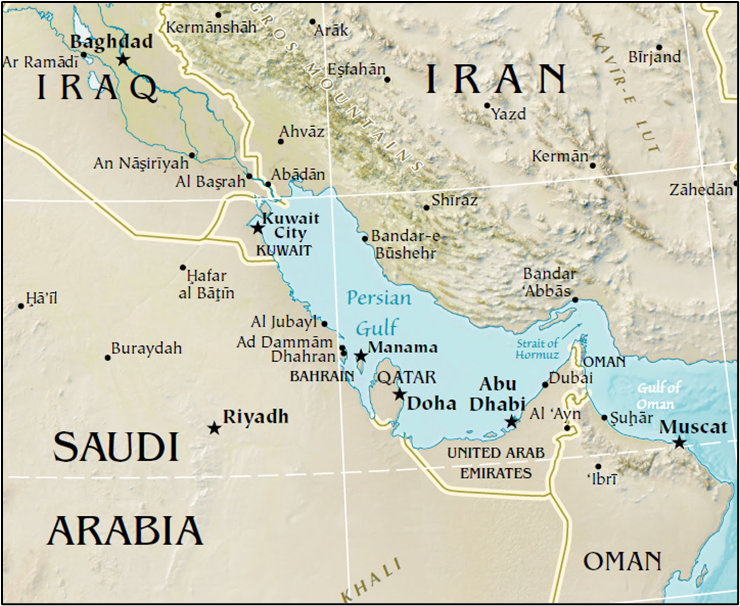
Persian Gulf – Geopolitically Critical Waters
The Persian Gulf, part of the Indian Ocean, lies between the Arabian Peninsula and Iran.
- It is bordered by Iraq, Bahrain, Qatar, Iran, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman
(Mnemonic: Iraq’s Big Queen Is Using Super Kool Oil) - Connects to Indian Ocean via the Strait of Hormuz.
- Rich in oil, dotted with islands like Qeshm, and receives sediments from Tigris-Euphrates-Karun rivers.
Can you locate all the eight countries bordered by Persian Gulf in the map below?
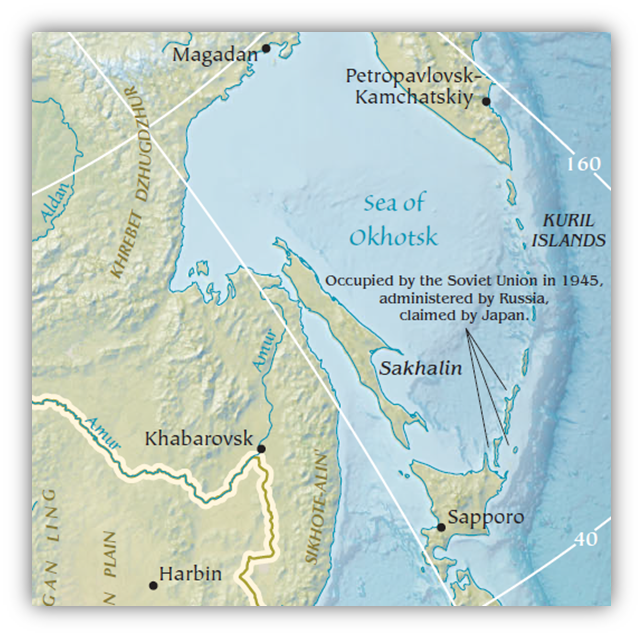
Sea of Okhotsk – Cold and Isolated
Situated in the northwest Pacific, almost fully enclosed by Russian land (except for a portion touching Hokkaido, Japan).
- Formed due to glaciation in the past two million years.
- Ecologically rich, but largely ice-covered in winters.
Central Asian Region – The Heart of the Steppe World
Central Asia stretches from the Caspian Sea to Western China, encompassing five countries:
- Kazakhstan (Astana)
- Uzbekistan (Tashkent)
- Turkmenistan (Ashgabat)
- Kyrgyzstan (Bishkek)
- Tajikistan (Dushanbe)
Key Features:
- Northern region: Grassy steppes
- Southern region: Aral Sea basin and deserts like Karakum (Turkmenistan) and Kyzylkum (Uzbekistan)
- Rivers like Amu Darya and Syr Darya originate from mountains in the east and flow northwest to the Aral Sea.
- Surrounded by Altai, Iranian and Afghan highlands, this region is geopolitically and historically rich (Silk Road region).

4 Comments