Understanding Galaxies and Dark Matter
So far, we’ve understood how the universe began, how it’s expanding, and what evidence supports this theory.
Now let’s zoom in and study the building blocks of the universe — Galaxies.
What is a Galaxy?
A galaxy is a massive system — made up of millions to billions of stars, along with gas, dust, and dark matter, all bound together by gravitational attraction.
Think of it like a giant cosmic city:
- Stars are like homes or buildings.
- Gas and dust clouds are like factories — where new stars are made.
- And the force of gravity is like the law-and-order system that keeps everything together 😊
📌 Fact Check:
- Smallest galaxies can have around 1 lakh stars (100,000),
- Largest galaxies can contain up to 3000 billion stars.
Classification of Galaxies
Among the billions of galaxies in the universe, astronomers have broadly classified them into:
A. Regular Galaxies
These have well-defined structures and are further divided into:
- Spiral Galaxies
- Elliptical Galaxies
B. Irregular Galaxies
- They don’t follow a defined shape.
- They make up around 1/10th of all galaxies.
- Stars in them tend to be very old.
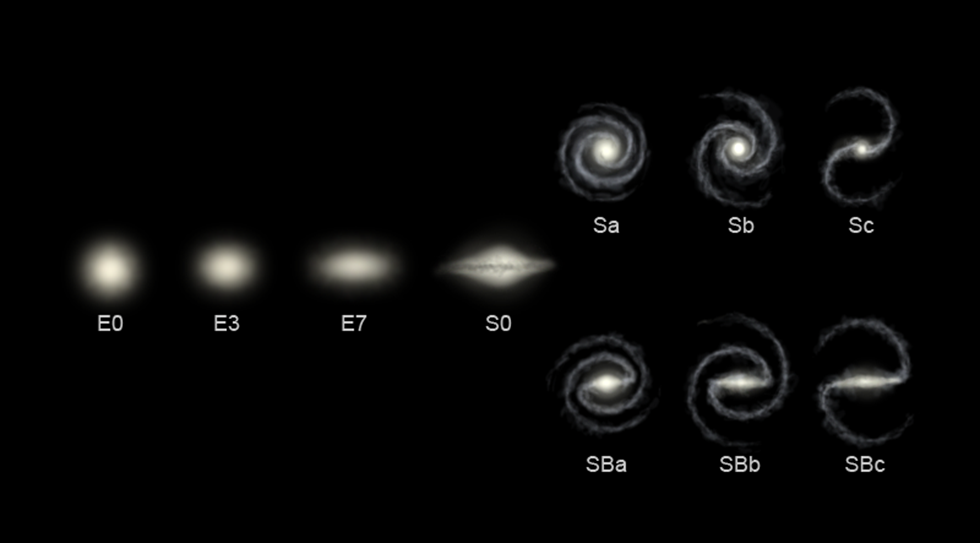
Regular Galaxies
🔹 Spiral Galaxies (e.g., Milky Way)
- These are disc-shaped with a central bulge and arms spiraling outwards.
- The centre has older stars, while the arms have young, bright stars.
- Rich in interstellar gas and dust, allowing new stars to keep forming.
- Star distribution is non-uniform.
- Usually smaller and less bright than elliptical galaxies.
🔹 Elliptical Galaxies
- These are oval or spherical in shape.
- Made up mostly of old stars.
- No new star formation occurs, as they lack interstellar gas.
- Generally larger and brighter than spiral galaxies.
- Some are even the brightest galaxies in the known universe.

The Mystery of Dark Matter
Now, here’s something fascinating and mysterious.
When scientists observed how spiral galaxies like the Milky Way rotate, they found something odd:
- Outer arms of the galaxy are rotating too fast — more than they should, given the visible mass.
- But according to Newton’s laws, this speed is only possible if there is more mass than what we can see.
🎯 This invisible mass is what scientists call Dark Matter.
🔹 What is Dark Matter?
- It makes up around 85% of all matter in the universe.
- It does not emit, absorb, or reflect light — hence the term “dark”.
- We cannot see it, but we know it exists due to its gravitational effects.
It’s like seeing leaves rustling on a tree — even if we can’t see the wind, we know it’s there.
Most of the dark matter is believed to be composed of unknown subatomic particles, yet to be discovered.
Total Composition of the Universe
This may surprise you:
- Dark energy + dark matter = 95.1% of the universe!
- That means all the stars, planets, humans, and everything we know — made of normal matter — comprise less than 5% of the universe.
We’re essentially living in a cosmic mystery — where 95% of the universe is invisible and unknown.
Our Galaxy: The Milky Way
Let’s now return home — to our own galaxy.
🔸 Basic Structure:
- The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy — like a disc with a bulging centre.
- Diameter: 1,50,000 to 2,00,000 light-years.
- Thickness:
- Central bulge: ~10,000 light years
- Disc: 500–2,000 light years
📌 A light year is not time but distance — the distance light travels in one year at the speed of 3 lakh km/sec.
For example, light from the Sun takes about 8.3 minutes to reach Earth.
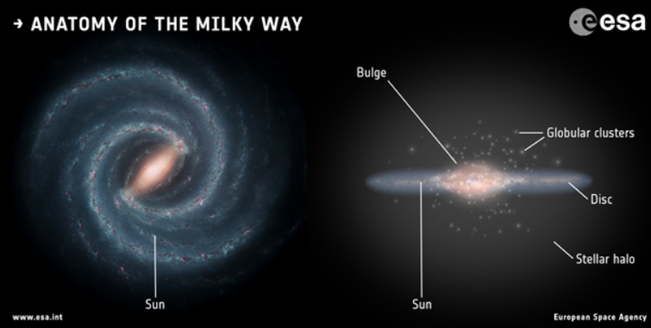
🔸 Key Features of the Milky Way:
- Contains 100–400 billion stars.
- Star movement: Inner stars rotate faster than outer ones.
- At the centre lies a supermassive black hole named Sagittarius A*.
- The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, about 26,000 light years from the centre — about one-third of the way out.
🔸 Types of Stars:
- Sun-like stars are actually rare in our galaxy.
- The most common stars are Red Dwarfs — smaller, dimmer, and cooler than our Sun.
🔸 Motion of the Sun:
- The Sun orbits the centre of the Milky Way.
- It takes about 220 million years to complete one full orbit — called a galactic year.
- Speed: Around 285 km/sec.
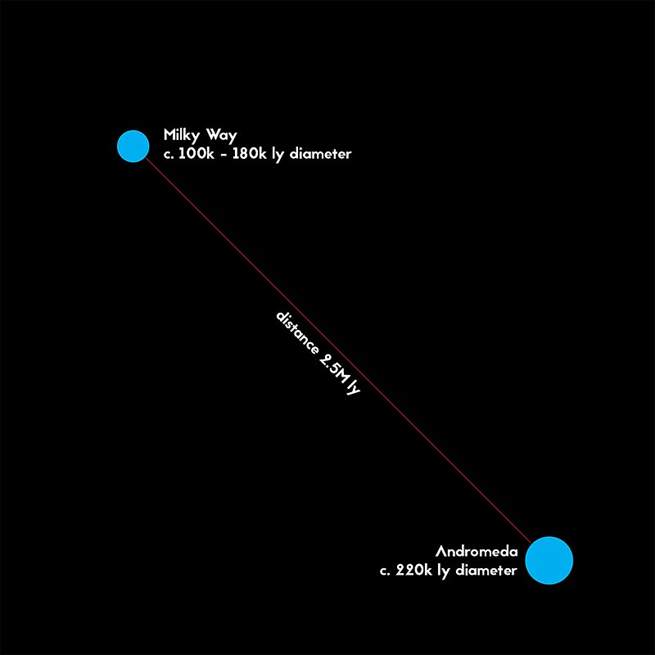
Neighbouring Galaxy: Andromeda
- Andromeda Galaxy is the nearest large galaxy to us.
- It is about 2 million light years away.
- One day, scientists believe, Milky Way and Andromeda may collide and merge, forming a new galaxy — though this will happen billions of years from now.
Conclusion: Galaxies — The Cosmic Architects
- Galaxies are the fundamental building blocks of the universe.
- They come in various shapes and sizes — each one holding a massive collection of stars, gas, and dust.
- Within these galaxies lies dark matter — invisible yet essential — holding the structure together through gravity.
- And in one corner of one such galaxy — the Milky Way — lies our tiny solar system, orbiting silently around a black hole, part of a vast and mysterious cosmos.
